Product Description
100HP 75KW Gas Powered Inverter CHINAMFG Rotary Screw Air Compressor for Welding
TECHNICAL DATA:
|
Model |
WZS-100EVA |
|
Air Flow/Working pressure |
13.2m3/min @ 8bar |
|
11.6m3/min @ 10bar |
|
|
Cooling type of COMPRESSOR |
Air cooling |
|
Cooling type of MOTOR |
Oil cooling |
|
Driven method |
Integrated connection |
|
Start way |
Soft VSD Start |
|
VSD inverter |
INOVANCE / HOLIP / VEICHI |
|
Exhaust Temp. |
< ambient temp. +8 degrees |
|
Oil content |
<2ppm |
|
Noise |
70±2 dB(A) |
|
Power |
380VAC/3ph/0~200Hz |
|
Motor power |
75kW/100hp |
|
Dimension |
2150*1100*1500mm |
|
Weight |
1650kg |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Horizontal |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Is the Fuel Efficiency of Gas Air Compressors?
The fuel efficiency of gas air compressors can vary depending on several factors, including the compressor’s design, engine size, load capacity, and usage patterns. Gas air compressors typically use internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or propane to generate the mechanical energy required for compressing air. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can influence the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors:
1. Engine Design and Size:
The design and size of the engine in a gas air compressor can impact its fuel efficiency. Engines with advanced technologies such as fuel injection and electronic controls tend to offer better fuel efficiency compared to older carbureted engines. Additionally, larger engines may consume more fuel to produce the required power, resulting in lower fuel efficiency compared to smaller engines for the same workload.
2. Load Capacity and Usage Patterns:
The load capacity and usage patterns of the gas air compressor play a significant role in fuel efficiency. Compressors operating at or near their maximum load capacity for extended periods may consume more fuel compared to compressors operating at lower loads. Additionally, compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks may have better fuel efficiency due to reduced demand on the engine.
3. Maintenance and Tuning:
Proper maintenance and tuning of the gas air compressor’s engine can improve fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance tasks such as oil changes, air filter cleaning/replacement, spark plug inspection, and tuning the engine to the manufacturer’s specifications can help ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
4. Operating Conditions:
The operating conditions, including ambient temperature, altitude, and humidity, can affect the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors. Extreme temperatures or high altitudes may require the engine to work harder, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Additionally, operating in humid conditions can affect the combustion process and potentially impact fuel efficiency.
5. Fuel Type:
The type of fuel used in the gas air compressor can influence its fuel efficiency. Gasoline and propane are common fuel choices for gas air compressors. The energy content and combustion characteristics of each fuel can affect the amount of fuel consumed per unit of work done. It is important to consider the specific fuel requirements and recommendations of the compressor manufacturer for optimal fuel efficiency.
6. Operator Skills and Practices:
The skills and practices of the operator can also impact fuel efficiency. Proper operation techniques, such as avoiding excessive idling, maintaining consistent engine speeds, and minimizing unnecessary load cycles, can contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
It is important to note that specific fuel efficiency ratings for gas air compressors can vary widely depending on the aforementioned factors. Manufacturers may provide estimated fuel consumption rates or fuel efficiency data for their specific compressor models, which can serve as a reference point when comparing different models or making purchasing decisions.
Ultimately, to maximize fuel efficiency, it is recommended to select a gas air compressor that suits the intended application, perform regular maintenance, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, and operate the compressor efficiently based on the workload and conditions.
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Operating Gas Air Compressors?
Operating gas air compressors safely is essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. It’s important to follow proper safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be taken when operating gas air compressors:
1. Read and Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Before operating a gas air compressor, carefully read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions, user manual, and safety guidelines. Follow the recommended procedures, maintenance schedules, and any specific instructions provided by the manufacturer.
2. Provide Adequate Ventilation:
Gas air compressors generate exhaust fumes and heat during operation. Ensure that the operating area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of exhaust gases, which can be harmful or even fatal in high concentrations. If operating indoors, use ventilation systems or open windows and doors to allow fresh air circulation.
3. Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating a gas air compressor. This may include safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and sturdy footwear. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, noise exposure, and hand injuries.
4. Perform Regular Maintenance:
Maintain the gas air compressor according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the compressor for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Keep the compressor clean and free from debris. Replace worn-out parts and components as needed to ensure safe and efficient operation.
5. Preventive Measures for Fuel Handling:
If the gas air compressor is powered by fuels such as gasoline, diesel, or propane, take appropriate precautions for fuel handling:
- Store fuel in approved containers and in well-ventilated areas away from ignition sources.
- Refuel the compressor in a well-ventilated outdoor area, following proper refueling procedures and avoiding spills.
- Handle fuel with caution, ensuring that there are no fuel leaks or spills near the compressor.
- Never smoke or use open flames near the compressor or fuel storage areas.
6. Use Proper Electrical Connections:
If the gas air compressor requires electrical power, follow these electrical safety precautions:
- Ensure that the electrical connections and wiring are properly grounded and in compliance with local electrical codes.
- Avoid using extension cords unless recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect electrical cords and plugs for damage before use.
- Do not overload electrical circuits or use improper voltage sources.
7. Secure the Compressor:
Ensure that the gas air compressor is securely positioned and stable during operation. Use appropriate mounting or anchoring methods, especially for portable compressors. This helps prevent tipping, vibrations, and movement that could lead to accidents or injuries.
8. Familiarize Yourself with Emergency Procedures:
Be familiar with emergency procedures and know how to shut off the compressor quickly in case of an emergency or malfunction. Have fire extinguishers readily available and know how to use them effectively. Develop an emergency action plan and communicate it to all personnel working with or around the compressor.
It’s crucial to prioritize safety when operating gas air compressors. By following these safety precautions and using common sense, you can minimize the risks associated with compressor operation and create a safer work environment for yourself and others.


editor by CX 2023-09-29
China OEM Factory Direct Sale 75kw 10bar Pm VSD Two-Stage Screw Air Compressor in China air compressor for sale
Product Description
Factory Direct Sale 75kW 10bar PM VSD Two-stage Screw Air Compressor in China
TECHNICAL DATA:
|
Model |
WZS-75PM-2S |
|
Air Flow/Working pressure |
16m3/min @ 8bar |
|
13m3/min @ 10bar |
|
|
Cooling type of COMPRESSOR |
Air cooling |
|
Cooling type of MOTOR |
Oil cooling |
|
Driven method |
Integrated connection |
|
Start way |
Soft VSD Start |
|
VSD inverter |
INOVANCE / HOLIP / VEICHI |
|
Exhaust Temp. |
< ambient temp. +8 degrees |
|
Oil content |
<2ppm |
|
Noise |
70±3 dB(A) |
|
Power |
380VAC/3ph/0~200Hz |
|
Motor power |
75kw/75hp |
|
Dimension |
2800*1750*1900mm |
|
Weight |
2800kg |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Horizontal |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

A Buyer’s Guide to Air Compressor Types
There are many types of Air Compressors, and it’s important to understand what each type has to offer. In this article, we’ll discuss single stage air compressors, low-noise compressors, and models with two pistons. But, before you buy an Air Compressor, be sure to read our buyer’s guide to the various types. This way, you’ll have all of the information you need to make the right decision for your business.
Single-stage air compressors
A single-stage air compressor is an excellent choice for most general-purpose purposes. They provide enough power to operate pneumatic tools, and they produce less heat. Single-stage air compressors, however, are not suitable for heavy-duty industrial uses. However, they can be used in various applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing facilities. They are also suitable for borewells and other high-pressure places.
These air compressors are a great choice for home use and are suitable for small-scale businesses, contractors, and small shops. These compressors have continuous duty cycles, cast iron compressor pumps, and a minimum 5,000-hour pump life. They also feature advanced features, including ODP motors, Auto Start & Controls, Receiver tanks, and power cords. They have low maintenance and can save you a great deal of money.
Single-stage air compressors are generally less expensive and lighter than their two-stage counterparts. Single-stage air compressors are also more portable, which is a plus for small projects. While two-stage compressors offer higher CFM, they are more powerful and bulky, making them unsuitable for small or home use. So it is essential to determine what you will use the air compressor for and decide on a model based on your needs.
A single-stage air compressor is made of a piston and a tank. The piston moves rapidly inside the cylinder and exerts pressure on the cylinder. This means that the piston can’t move any faster than the air pressure outside the cylinder. The piston is designed to operate in the same way for each stage. This is a great choice for home shops and one-man automotive shops, as it allows you to control the pressure without sacrificing the pump’s life.
Single-stage air compressors are often cheaper than two-stage versions, but they are not the best choice for every application. If you are only using your air compressor occasionally, you’ll find a one-stage model to be much more reliable than a two-stage model. The main difference between the two types of compressors is in the amount of air that each stage compresses. A two-stage air compressor will have more air storage capacity, but it will still produce more pressure.
Rotary vane compressors
Rotary vane compressors use a centrifugal pump to compress air. The rotor is set eccentrically in the housing, which almost touches the vane. As the rotor turns, the air that enters the pump is trapped between the vanes. This compressed air undergoes compression as the rotor rotates. Vanes are small pieces of carbon fiber or graphite composite. Vanes may be made of different materials depending on the application.
While rotary vane pumps are not commonly used to produce compressed air, they are widely used in automotive and hydraulic applications. Chances are, you have used a rotary vane pump at some point in your life. These pumps are also common in the vacuum and compressed air industries. As a result, many people don’t realize that they’re still around. They feature slots that allow the vanes to slide in and out of the rotor.
A rotary vane compressor has a drum and rotor inside. The rotor is eccentrically positioned and has slots and grooves on its surface. Its inlet and outlet ports are situated off-center, allowing the vanes to be pushed out by centrifugal force. Because the rotor rotates so quickly, air is trapped between the vanes. This air then becomes pressurized by the rotating rotor.
Rotating vane compressors can be easily serviced and repaired. A simple replacement of carbon vanes requires just 15 minutes and common tools. The carbon vanes typically last nine to eighteen months, depending on system operating pressure. Before purchasing a rotary vane compressor, make sure to check whether it has been properly performance-tested and has a warranty. Generally, warranties cover the rotor/stator chambers but do not cover the vanes or air filters. You should also check if the unit is covered by a lightning or water damage warranty.
Rotary vane compressors are an integral part of manufacturing industries. Many pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities depend on rotary vane compressors to control their equipment. Other industries that use rotary vane compressors include the plastics, woodworking, natural gas, and medical & dental fields. Their benefits are numerous and far outweigh any disadvantages of rotary screw compressors. For example, a rotary vane compressor can double the life of a conventional compressor.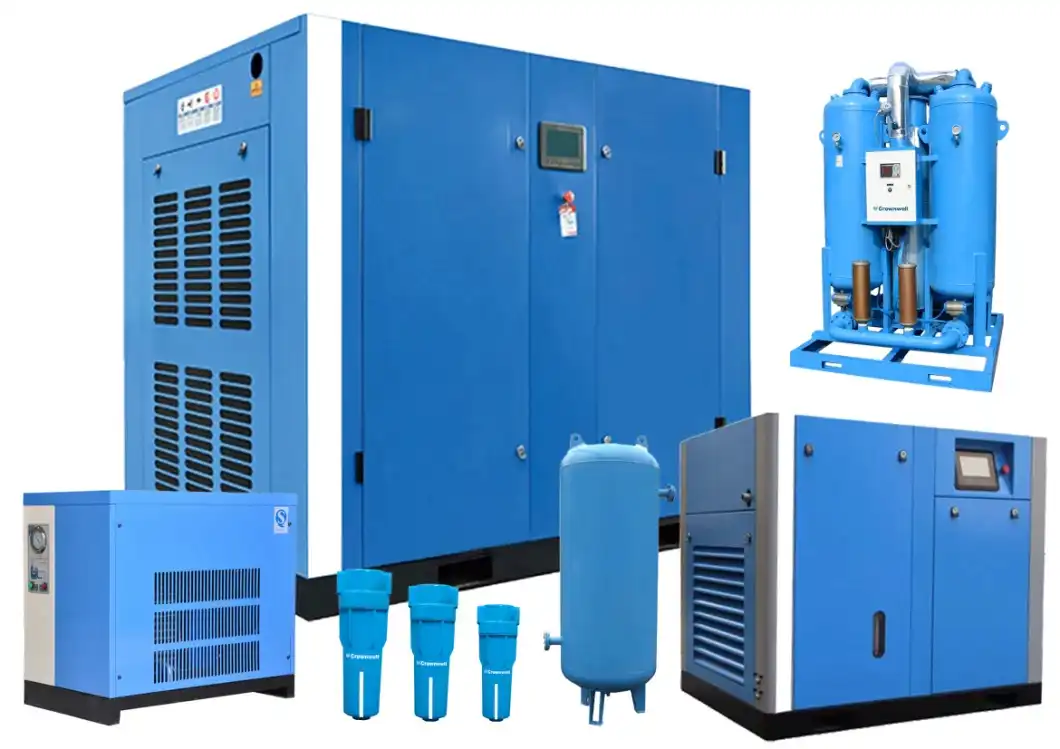
Rotary vane compressors with low-noise models
If you are looking for a rotary vane air compressor, you have come to the right place. CZPT’s LV Series rotary vane compressors offer low-noise models, compact size, and robust integration. In addition to their low-noise features, they feature large filter systems to deliver high-quality compressed air. The LV Series models also feature CZPT’s reputation for reliability and quality.
This type of compressor uses centrifugal force to operate and is limited in its top and minimum operating speeds. They are only a third as powerful as screw compressors, and their top speed limits are much lower. Furthermore, the vanes wear out easily at high speeds because there is not enough centrifugal force to seal them against the cylinder’s edges. Even at half their full capacity, they consume as much as 80% of their total energy rating.
Because piston compressors produce a lot of noise, factory owners and shop owners have begun to install noise-dampening cabinets and other solutions. But, rotary vane compressors produce far less noise than a traditional vacuum, and the maintenance costs are also low. Rotary vane compressors are also extremely helpful in several industries. They are used in the automotive and auto finishing industries, as well as in dairy industries and milking machines.
If you have a deep pond, a rotary vane air compressor kit can pump up to 20 feet of water. This is more than enough airflow for two to five diffusers. A 1/4 HP rotary vane kit pumps around 4.2 CFM. It also helps to increase circulation and oxygen levels in the pond. Finally, a 1/4 HP kit offers the necessary power to clean up the bottom of a pond.
The rotary vane and rotary screw are the most popular air compressors today. While they are similar in many ways, they are more versatile and durable than their counterparts. They use fewer angular contact ball bearings and require less frequent maintenance than piston air compressors. Compared to piston air compressors, rotary vane and rotary screw compressors are quieter and are less expensive.
Rotary vane compressors with two pistons
The rotary vane and rotary screw compressors are similar in application, but both have different advantages and disadvantages. This article will compare the benefits of each and highlight the differences between them. While both are commonly used in industrial applications, rotary vane compressors are preferred by many industries. These compressors also have a wide range of uses, ranging from automotive air tool operation to milking machines. These compressors also have the advantage of being quieter than piston-powered ones.
The current common rail position may not be suitable for pressure swirl injectors, but new positions have been tested and show improvements in specific energy values. Moreover, the current position is not required for external oil pumps. However, mass induction and expulsion have to be performed with utmost care. This article focuses on the design and efficiency of rotary vane compressors. You can find more information about this new design in the references mentioned below.
The advantages of this type of compressor are its low cost, compact size, and easy maintenance. Hence, they are preferred in low capacity applications. Moreover, they feature integrated vanes. The rotating vanes close the air gap and compress air towards the outlet. Compared to piston-powered compressors, these units are cheaper and more reliable. Therefore, you should choose one with the lowest price tag. You can also opt for rotary vane compressors that are oil-free.
Sliding vane compressors are another popular variant. They have a single cylinder connected to the compressor and are capable of operating at low speeds. This design also reduces the amount of friction and maintains volumetric efficiency. However, the sliding vane compressors suffer from high frictional losses. If you are looking for a more efficient rotary compressor, this is the best option. While sliding vane compressors have been in the spotlight for over a century, they are still quite young.
These compressors are easy to install and maintain. They are also quieter than piston compressors. They are also cheaper than piston-driven compressors. The energy efficiency and low price make them the perfect choice for any commercial or industrial application. If you’re looking for a small, compact compressor, the rotary vane has been proven to be the best choice for your needs. You should know that it has a long service life.


editor by CX 2023-06-09
China Textile Industry Low Pressure 75kw 5bar Two-Stage Pm VSD/VFD Rotary Screw Air Compressor, Energy Saving45%, OEM&Customization Provided air compressor oil
Merchandise Description
Textile Market Minimal Force 75kw 5bar Two-Phase Pm VSD/VFD Rotary Screw Air Compressor, Power Saving45%, OEM&Customization Supplied
Specialized Info:
| Product | (kw) Energy |
Air folw/pressure | Outlet dimensions | Sounds | KG Device weight |
mm Device measurement |
| WZS-22PMD-2S | 22 | six.25m³/.5MPa | RP1 1/two | 66±3 | 1350 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-30PMD-2S | 30 | seven.2m³/.5MPa | RP1 1/two | 66±3 | 1550 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-37PMD-2S | 37 | 10m³/.5MPa | RP1 1/two | 68±3 | 1900 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-45PMD-2S | forty five | 12m³/.5MPa | RP2 | 68±3 | 2100 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-55PMD-2S | fifty five | thirteen.8m³/.5MPa | RP2 | 70±3 | 2200 | 2100x1360x1660 |
| WZS-75PMD-2S | 75 | eighteen.5m³/.5MPa | DN65 | 70±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-90PMD-2S | 90 | 23m³/.5MPa | DN65 | 72±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-110PMD-2S | 110 | 28m³/.5MPa | DN80 | 72±3 | 3200 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-132PMD-2S | 132 | 32.5m³/.5MPa | D270N80 | 72±3 | 3500 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-160PMD-2S | a hundred and sixty | 41m³/.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4100 | 3200x1750x2350 |
| WZS-185PMD-2S | 185 | 45m³/.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4500 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-200PMD-2S | 200 | 50m³/.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 5100 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-220PMD-2S | 220 | 54m³/.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 6200 | 3800x2250x2250 |
| WZS-250PMD-2S | 250 | 61m³/.5MPa | DN150 | 78±3 | 6600 | 4200x2250x2400 |
FAQ
1. OEM/ODM, or customer’ s symbol printed is offered?
Yes, OEM/ODM, customer’s logo is welcomed.
two. Delivery day?
Usually 5-25 doing work times following getting deposit, certain shipping and delivery day based mostly on purchase quantity.
three. What is actually your payment conditions?
Regularly undertaking thirty% deposit and 70% stability by T/T, Western Union, Paypal, other payment conditions also can be reviewed primarily based on our cooperation.
4. How to handle your top quality?
We have professional QC team, manage the quality in the course of the mass generation and inspect the goods before shipping and delivery.
five. If we don’ t have shipping and delivery forwarder in China , would you do this for us?
We can offer you you ideal delivery line to make certain you can get the items well timed at ideal value.
six. I in no way occur to China just before , can you be my CZPT in China?
Sure , I’m happy to be your CZPT because our organization straight located in ZheJiang , where is the most well-known metropolis in China, if you want to come China then we are happy to give you one-quit provider, such as booking ticket, selecting up at the airport, reserving lodge, accompany browsing manufacturing unit. It gonna make you an unforgettable memory.
|
US $10,000-20,000 / Unit | |
1 Unit (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Video Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Unit 1 Year, Air End 2 Years |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Model | (kw) Power |
Air folw/pressure | Outlet size | Noise | KG Unit weight |
mm Unit size |
| WZS-22PMD-2S | 22 | 6.25m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 66±3 | 1350 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-30PMD-2S | 30 | 7.2m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 66±3 | 1550 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-37PMD-2S | 37 | 10m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 68±3 | 1900 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-45PMD-2S | 45 | 12m³/0.5MPa | RP2 | 68±3 | 2100 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-55PMD-2S | 55 | 13.8m³/0.5MPa | RP2 | 70±3 | 2200 | 2100x1360x1660 |
| WZS-75PMD-2S | 75 | 18.5m³/0.5MPa | DN65 | 70±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-90PMD-2S | 90 | 23m³/0.5MPa | DN65 | 72±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-110PMD-2S | 110 | 28m³/0.5MPa | DN80 | 72±3 | 3200 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-132PMD-2S | 132 | 32.5m³/0.5MPa | D270N80 | 72±3 | 3500 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-160PMD-2S | 160 | 41m³/0.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4100 | 3200x1750x2350 |
| WZS-185PMD-2S | 185 | 45m³/0.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4500 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-200PMD-2S | 200 | 50m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 5100 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-220PMD-2S | 220 | 54m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 6200 | 3800x2250x2250 |
| WZS-250PMD-2S | 250 | 61m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 78±3 | 6600 | 4200x2250x2400 |
|
US $10,000-20,000 / Unit | |
1 Unit (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Video Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Unit 1 Year, Air End 2 Years |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Model | (kw) Power |
Air folw/pressure | Outlet size | Noise | KG Unit weight |
mm Unit size |
| WZS-22PMD-2S | 22 | 6.25m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 66±3 | 1350 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-30PMD-2S | 30 | 7.2m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 66±3 | 1550 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-37PMD-2S | 37 | 10m³/0.5MPa | RP1 1/2 | 68±3 | 1900 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-45PMD-2S | 45 | 12m³/0.5MPa | RP2 | 68±3 | 2100 | 1800x1270x1550 |
| WZS-55PMD-2S | 55 | 13.8m³/0.5MPa | RP2 | 70±3 | 2200 | 2100x1360x1660 |
| WZS-75PMD-2S | 75 | 18.5m³/0.5MPa | DN65 | 70±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-90PMD-2S | 90 | 23m³/0.5MPa | DN65 | 72±3 | 2800 | 2800x1750x1900 |
| WZS-110PMD-2S | 110 | 28m³/0.5MPa | DN80 | 72±3 | 3200 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-132PMD-2S | 132 | 32.5m³/0.5MPa | D270N80 | 72±3 | 3500 | 3200x1750x2250 |
| WZS-160PMD-2S | 160 | 41m³/0.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4100 | 3200x1750x2350 |
| WZS-185PMD-2S | 185 | 45m³/0.5MPa | DN125 | 74±3 | 4500 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-200PMD-2S | 200 | 50m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 5100 | 3800x2150x2250 |
| WZS-220PMD-2S | 220 | 54m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 76±3 | 6200 | 3800x2250x2250 |
| WZS-250PMD-2S | 250 | 61m³/0.5MPa | DN150 | 78±3 | 6600 | 4200x2250x2400 |
Choosing the Right Air Compressor For Your Home
You will find that air compressors are indispensable tools for a variety of situations, including garages, home workshops, and basements. These tools can power a variety of tools, and each model is sized to suit the job at hand. Because air compressors have only one motor, they are lightweight, compact, and easy to handle. Using one air compressor to power several tools will also reduce the wear and tear on individual components. This article will introduce some important characteristics to look for when choosing the right air compressor for your home.
Positive displacement
A positive displacement compressor applies pressure to a fluid, whereas a centrifugal one does the opposite. A positive displacement compressor creates the desired pressure by trapping air and increasing its volume. Its discharge valve releases the high-pressure gas. These compressors are used in industrial applications and nuclear power plants. The difference between a positive and negative displacement compressor is that a positive displacement compressor can compress and release air at a consistent rate.
A positive displacement air compressor uses a reciprocating piston to compress air. This reduces the volume of the air in the compression chamber, and a discharge valve opens when the pressure reaches the desired level. These compressors are used in bicycle pumps and other pneumatic tools. Positive displacement air compressors have multiple inlet ports and have several configurations. Positive displacement air compressors have a single-acting and double-acting piston, and can be oil-lubricated or oil-free.
A positive displacement air compressor is different from a dynamic compressor. It draws air into the compression chambers and then releases the pressure when the valve is opened. Positive displacement compressors are common in industrial applications and are available in single-acting, double-acting, and oil-lubricated models. Large piston compressors have ventilated intermediate pieces and crossheads on gudgeon pins. Smaller models have permanently sealed crankcases with bearings.
Oil-free
Oil-free air compressors have some advantages over their oil-lubricated counterparts. They do not require lubrication oil because they are coated with Teflon. The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction and is layered, so it slides past other layers with little effort. Because of this, oil-free compressors tend to be cheaper and still deliver comparable performance. Oil-free compressors are a good choice for industrial applications.
The life of an oil-free air compressor is significantly longer than an oil-lubricated counterpart. These models can operate up to 2,000 hours, four times longer than the average oil-lubed compressor. Oil-free compressors also have a significantly lower operating noise than their oil-lubricated counterparts. And because they don’t need oil changes, they are quieter. Some even last up to 2,000 hours.
An oil-free air compressor is a good choice if your application requires high levels of purity. Several applications require ultra-pure air, and even a drop of oil can cause product spoilage or damage to production equipment. In addition to the health risks, an oil-free air compressor reduces the costs associated with oil contamination and minimizes leaks. It also eliminates the need for oil collection, disposal, and treatment.
A typical oil-free air compressor is very efficient, requiring only about 18% of the full load horsepower. However, oil-free compressors have a higher risk of premature failure and are not recommended for large-scale industrial applications. They may also use up to 18% of the compressor’s full capacity. They may sound appealing, but you must make sure you understand the benefits of an oil-free air compressor before choosing one for your industrial applications.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor is designed to provide the power for a single pneumatic tool or device. These machines are generally smaller than two-stage compressors and produce less heat and energy. These machines aren’t designed for heavy-duty industries, but they are still highly effective for a variety of applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing plants. They can also be used in borewells, as they are suitable for small spaces with low air flow requirements.
A single-stage air compressor has one cylinder and two valves – the inlet and the delivery valves. Both of these valves function mechanically, with the inlet valve controlling torque and the delivery one controlling air pressure. Generally, single-stage compressors are powered by a gas engine, but there are also electric models available. The single-stage air compressor is the most common type of air compressor. It has a single cylinder, one piston, and one air cylinder.
The single-stage air compressors are used for small projects or personal use. A two-stage air compressor is more effective for industrial projects. Its longer air end life makes it more efficient. It is also more efficient for use in the automotive industry, where the engine has many cylinders. In general, single-stage compressors require a higher power level. The single-stage model is ideal for small projects, while a two-stage one is suitable for larger-scale arsenals.
CFM
The cubic foot-per-minute (CFM) of an air compressor is the output of the machine. In order to calculate the CFM level, start by looking at the compressor’s specifications. You should know how many cubic feet the unit can hold and how many pounds per square inch it can compress. Once you have these information, you can calculate the CFM. Now you can use these numbers to select an appropriate air compressor for your needs.
The most common way to increase the CFM of an air compressor is to turn the regulator down. By turning the dial down, the air compressor will produce more than 10 CFM. You can also try connecting two output valves. Make sure that the settings are adjusted properly before you begin. This will ensure that your air compressor is functioning at its maximum efficiency and lifespan. To increase the CFM of your air compressor, first check that your regulator is calibrated for the desired pressure level.
To calculate the CFM of an air compressor, first determine the tank volume of the machine. Then, multiply this volume by the time it takes to fill the tank. Then, divide the result by 60 seconds to calculate the CFM. Once you know how much air your machine can hold, you can choose a suitable air compressor. If you’re working in a confined area, you should buy a tool with a large tank.
PSI
The PSI of an air compressor is the pressure that it can output. A typical air compressor has a gauge connected to the airline at the bottom, next to it, or between the two. The gauge tells the actual pressure of the air compressor, while the cut-out pressure is determined by the manufacturer. The manufacturer recommends that you set the cut-out pressure twenty to forty PSI higher than the factory recommended pressure. If you want to set the pressure for your nail gun, you can use the cut-in and cut-out pressures on your compressor, and the tank won’t exceed this range.
The PSI of an air compressor measures the force that it can deliver, which is often in pounds per square inch. For most air tools, you need at least forty to 90 psi. In general, reciprocating air compressors work on an on/off basis. This relationship is known as the duty cycle. All air compressors are rated for a particular duty cycle, such as fifty percent on and twenty-five percent off.
The Psig of an air compressor is not free, as many people believe. The PSI of an air compressor is not free, but it is essential to maintain it for safe operations. If you’re having trouble maintaining a consistent pressure, consider turning down the PSI of your compressor by 2 psig. This will determine the critical pressure for the machine. You’ll also increase the amount of energy in the system by one percent.
Power source
The power source for an air compressor is crucial in its operation. Without the correct voltage and amperage, air compressors will not function properly. The power source must be close to the compressor so that it can plug into an electrical outlet. If it is too far from the outlet, the compressor may not be able to build enough pressure. When this happens, the fuse inside the air compressor will turn off to protect the user. The power source should be a safe distance from the compressor.
Most manufacturers do not specify the power source for an air compressor. Depending on the horsepower, the compressor will require approximately four amps of power. A one-horsepower compressor would draw about twelve amps. If it were powered by a typical 120-volt household supply, its motor would exceed the 15-amp breaker capacity. A larger air compressor, however, will require a separate 15-amp power source, making it impossible to use it with this type of power source.
The power source for an air compressor is typically electrical alternating current (AC) that is equivalent to the voltage on a standard wall outlet. A three-phase air compressor, on the other hand, requires a special AC supply with three electrical offset pulses. Regardless of the type of air compressor, the power source must be compatible with the incoming power service. One of the most common problems when attempting to connect an air compressor to an AC power source is undersized wire. This results in low voltage and high amperes, tripping of over-load relays and blown fuses.


editor by czh 2022-12-19