Product Description
Product Description
| Product Name | Auto A/C Compressor |
| Application | Auto Air-Conditioning System |
| Certification | IATF16949,ISO14 92610VW200 92610-VW200 |
| Bailin NO | N/A |
Company Profile
| After-sales Service: | 24 Hour on-Line |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Classification: | AC Compressor |
| Samples: |
US$ 199/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
What is the role of air compressors in power generation?
Air compressors play a significant role in power generation, supporting various operations and equipment within the industry. Here are some key roles of air compressors in power generation:
1. Combustion Air Supply:
Air compressors are used to supply compressed air for the combustion process in power generation. In fossil fuel power plants, such as coal-fired or natural gas power plants, compressed air is required to deliver a steady flow of air to the burners. The compressed air helps in the efficient combustion of fuel, enhancing the overall performance and energy output of the power plant.
2. Instrumentation and Control:
Air compressors are utilized for instrumentation and control systems in power generation facilities. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic control valves, actuators, and other pneumatic devices that regulate the flow of steam, water, and gases within the power plant. The reliable and precise control provided by compressed air ensures efficient and safe operation of various processes and equipment.
3. Cooling and Ventilation:
In power generation, air compressors are involved in cooling and ventilation applications. Compressed air is used to drive air-operated cooling fans and blowers, providing adequate airflow for cooling critical components such as generators, transformers, and power electronics. The compressed air also assists in maintaining proper ventilation in control rooms, substations, and other enclosed spaces, helping to dissipate heat and ensure a comfortable working environment.
4. Cleaning and Maintenance:
Air compressors are employed for cleaning and maintenance tasks in power generation facilities. Compressed air is utilized to blow away dust, dirt, and debris from equipment, machinery, and electrical panels. It helps in maintaining the cleanliness and optimal performance of various components, reducing the risk of equipment failure and improving overall reliability.
5. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
In power generation plants, air compressors provide the necessary compressed air for operating pneumatic tools and equipment. These tools include impact wrenches, pneumatic drills, grinders, and sandblasting equipment, which are utilized for installation, maintenance, and repair tasks. The high-pressure air generated by compressors enables efficient and reliable operation of these tools, enhancing productivity and reducing manual effort.
6. Nitrogen Generation:
Sometimes, air compressors are used in power generation for nitrogen generation. Compressed air is passed through a nitrogen generator system, which separates nitrogen from other components of air, producing a high-purity nitrogen gas stream. Nitrogen is commonly used in power plant applications, such as purging systems, blanketing in transformers, and generator cooling, due to its inert properties and low moisture content.
7. Start-up and Emergency Systems:
Air compressors are an integral part of start-up and emergency systems in power generation. Compressed air is utilized to power pneumatic starters for gas turbines, providing the initial rotation needed to start the turbine. In emergency situations, compressed air is also used to actuate emergency shutdown valves, safety systems, and fire suppression equipment, ensuring the safe operation and protection of the power plant.
Overall, air compressors contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of power generation facilities, supporting combustion processes, control systems, cooling, cleaning, and various other applications critical to the power generation industry.
.webp)
Can air compressors be integrated into automated systems?
Yes, air compressors can be integrated into automated systems, providing a reliable and versatile source of compressed air for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how air compressors can be integrated into automated systems:
Pneumatic Automation:
Air compressors are commonly used in pneumatic automation systems, where compressed air is utilized to power and control automated machinery and equipment. Pneumatic systems rely on the controlled release of compressed air to generate linear or rotational motion, actuating valves, cylinders, and other pneumatic components. By integrating an air compressor into the system, a continuous supply of compressed air is available to power the automation process.
Control and Regulation:
In automated systems, air compressors are often connected to a control and regulation system to manage the compressed air supply. This system includes components such as pressure regulators, valves, and sensors to monitor and adjust the air pressure, flow, and distribution. The control system ensures that the air compressor operates within the desired parameters and provides the appropriate amount of compressed air to different parts of the automated system as needed.
Sequential Operations:
Integration of air compressors into automated systems enables sequential operations to be carried out efficiently. Compressed air can be used to control the timing and sequencing of different pneumatic components, ensuring that the automated system performs tasks in the desired order and with precise timing. This is particularly useful in manufacturing and assembly processes where precise coordination of pneumatic actuators is required.
Energy Efficiency:
Air compressors can contribute to energy-efficient automation systems. By incorporating energy-saving features such as Variable Speed Drive (VSD) technology, air compressors can adjust their power output according to the demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of low activity. Additionally, efficient control and regulation systems help optimize the use of compressed air, minimizing waste and improving overall energy efficiency.
Monitoring and Diagnostics:
Integration of air compressors into automated systems often includes monitoring and diagnostic capabilities. Sensors and monitoring devices can be installed to collect data on parameters such as air pressure, temperature, and system performance. This information can be used for real-time monitoring, preventive maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring the reliable operation of the automated system.
When integrating air compressors into automated systems, it is crucial to consider factors such as the specific requirements of the automation process, the desired air pressure and volume, and the compatibility of the compressor with the control and regulation system. Consulting with experts in automation and compressed air systems can help in designing an efficient and reliable integration.
In summary, air compressors can be seamlessly integrated into automated systems, providing the necessary compressed air to power and control pneumatic components, enabling sequential operations, and contributing to energy-efficient automation processes.
.webp)
In which industries are air compressors widely used?
Air compressors find extensive usage across various industries due to their versatility and ability to generate compressed air. Here are some industries where air compressors are widely employed:
1. Manufacturing: Air compressors are essential in manufacturing processes for powering pneumatic tools and equipment. They are used for tasks such as operating assembly lines, powering robotic machinery, running paint sprayers, and driving pneumatic actuators.
2. Construction: Air compressors play a crucial role in the construction industry. They power pneumatic tools like jackhammers, nail guns, impact wrenches, and concrete breakers. Compressed air is also used for concrete spraying, sandblasting, and operating air-powered lifts and hoists.
3. Automotive: Air compressors are widely used in automotive manufacturing and repair. They power air tools used in auto body shops, tire inflation equipment, pneumatic lifts, and air-operated brake systems. Compressed air is also utilized in vehicle painting and drying processes.
4. Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry extensively relies on air compressors for various applications. They are used for pneumatic drilling, powering pneumatic tools in refineries and petrochemical plants, operating pneumatic valves and actuators, and providing instrument air for control systems.
5. Food and Beverage: Air compressors are employed in the food and beverage industry for tasks such as packaging, bottling, and sealing. They power pneumatic conveying systems, control air pressure in food processing equipment, and provide clean compressed air for food handling and storage.
6. Pharmaceutical and Healthcare: Air compressors find application in pharmaceutical manufacturing and healthcare facilities. They are used for operating medical equipment, such as ventilators and dental tools. Compressed air is also utilized in pharmaceutical processes, including tablet coating, fluid bed drying, and aseptic packaging.
7. Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies on air compressors for various applications, including aircraft maintenance and assembly. They power pneumatic tools for aircraft repair, provide compressed air for cleaning and pressurizing systems, and support ground operations, such as tire inflation and aircraft de-icing.
8. Mining: Air compressors are extensively used in the mining industry. They power pneumatic tools for drilling, rock blasting, and excavation. Compressed air is also utilized for ventilation, conveying materials, and operating underground equipment.
9. Energy and Utilities: Air compressors play a vital role in the energy and utilities sector. They are used in power generation plants for pneumatic control systems, instrument air, and operating pneumatic valves. Compressed air is also employed for cleaning and maintenance purposes.
These are just a few examples of the industries where air compressors are widely utilized. The versatility and reliability of air compressors make them indispensable in numerous applications across diverse sectors.


editor by CX 2023-10-11
China high quality 10PA17c Type Air Condition Compressor 0K55261450b 0K2kb61450 for KIA/Hyundai 2.0 air compressor parts
Product Description
Product Description
| Product Name | 10PA17C type air condition compressor 0K55261450B 0K2KB61450 for KIA/HYUNDAI 2.0 |
| Application | HYUNDAI TUCSON Car Air-Conditioning System |
| Certification | IATF16949,ISO14001 |
| Car Model | HYUNDAI TUCSON |
| Clutch | 118mm PV6 |
| Refrigeration | R134a |
| Volt | 12V |
| OE NO | 0K55261450B 0K2KB61450 |
| Bailin NO | BL.86.02 |
Company Profile
contact-info.html
| After-sales Service: | 24 Hour on-Line |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Classification: | AC Compressor |
| Job Classification: | Standard |
| Transmission Power: | Internal-combustion Engine |
| Cooling Method: | Air-cooled |
| Samples: |
US$ 99/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How are air compressors utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Air compressors play a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where they are utilized for various critical applications. The pharmaceutical industry requires a reliable source of clean and compressed air to ensure the safety, efficiency, and quality of its processes. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing:
1. Manufacturing Processes:
Air compressors are used in numerous manufacturing processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Compressed air is employed for tasks such as mixing and blending of ingredients, granulation, tablet compression, coating, and encapsulation of pharmaceutical products. The controlled delivery of compressed air facilitates precise and consistent manufacturing processes, ensuring the production of high-quality pharmaceuticals.
2. Instrumentation and Control Systems:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities rely on compressed air for powering instrumentation and control systems. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic valves, actuators, and control devices that regulate the flow of fluids, control temperature and pressure, and automate various processes. The clean and dry nature of compressed air makes it ideal for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of these critical control mechanisms.
3. Packaging and Filling:
Air compressors are employed in pharmaceutical packaging and filling processes. Compressed air is used to power machinery and equipment for bottle cleaning, labeling, capping, and sealing of pharmaceutical products. Compressed air provides the necessary force and precision for efficient and reliable packaging, ensuring product safety and compliance.
4. Cleanroom Environments:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing often takes place in controlled cleanroom environments to prevent contamination and maintain product quality. Air compressors are used to supply clean and filtered compressed air to these cleanrooms, ensuring a controlled and sterile environment for the production of pharmaceuticals. Compressed air is also utilized in cleanroom air showers and air curtains for personnel and material decontamination.
5. Laboratory Applications:
In pharmaceutical laboratories, air compressors are utilized for various applications. Compressed air is used in laboratory instruments, such as gas chromatographs, mass spectrometers, and other analytical equipment. It is also employed in clean air cabinets, fume hoods, and laminar flow benches, providing a controlled and clean environment for testing, analysis, and research.
6. HVAC Systems:
Air compressors are involved in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. Compressed air powers the operation of HVAC controls, dampers, actuators, and air handling units, ensuring proper air circulation, temperature control, and environmental conditions in various manufacturing areas.
By utilizing air compressors in pharmaceutical manufacturing, the industry can maintain strict quality standards, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
.webp)
Are there differences between single-stage and two-stage air compressors?
Yes, there are differences between single-stage and two-stage air compressors. Here’s an in-depth explanation of their distinctions:
Compression Stages:
The primary difference between single-stage and two-stage air compressors lies in the number of compression stages they have. A single-stage compressor has only one compression stage, while a two-stage compressor has two sequential compression stages.
Compression Process:
In a single-stage compressor, the entire compression process occurs in a single cylinder. The air is drawn into the cylinder, compressed in a single stroke, and then discharged. On the other hand, a two-stage compressor utilizes two cylinders or chambers. In the first stage, air is compressed to an intermediate pressure in the first cylinder. Then, the partially compressed air is sent to the second cylinder where it undergoes further compression to reach the desired final pressure.
Pressure Output:
The number of compression stages directly affects the pressure output of the air compressor. Single-stage compressors typically provide lower maximum pressure levels compared to two-stage compressors. Single-stage compressors are suitable for applications that require moderate to low air pressure, while two-stage compressors are capable of delivering higher pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications that require greater air pressure.
Efficiency:
Two-stage compressors generally offer higher efficiency compared to single-stage compressors. The two-stage compression process allows for better heat dissipation between stages, reducing the chances of overheating and improving overall efficiency. Additionally, the two-stage design allows the compressor to achieve higher compression ratios while minimizing the work done by each stage, resulting in improved energy efficiency.
Intercooling:
Intercooling is a feature specific to two-stage compressors. Intercoolers are heat exchangers placed between the first and second compression stages. They cool down the partially compressed air before it enters the second stage, reducing the temperature and improving compression efficiency. The intercooling process helps to minimize heat buildup and reduces the potential for moisture condensation within the compressor system.
Applications:
The choice between a single-stage and two-stage compressor depends on the intended application. Single-stage compressors are commonly used for light-duty applications such as powering pneumatic tools, small-scale workshops, and DIY projects. Two-stage compressors are more suitable for heavy-duty applications that require higher pressures, such as industrial manufacturing, automotive service, and large-scale construction.
It is important to consider the specific requirements of the application, including required pressure levels, duty cycle, and anticipated air demand, when selecting between a single-stage and two-stage air compressor.
In summary, the main differences between single-stage and two-stage air compressors lie in the number of compression stages, pressure output, efficiency, intercooling capability, and application suitability.
.webp)
How do oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ?
Oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ in terms of their lubrication systems and the presence of oil in their operation. Here are the key differences:
Oil-Lubricated Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-lubricated air compressors use oil for lubricating the moving parts, such as pistons, cylinders, and bearings. The oil forms a protective film that reduces friction and wear, enhancing the compressor’s efficiency and lifespan.
2. Performance: Oil-lubricated compressors are known for their smooth and quiet operation. The oil lubrication helps reduce noise levels and vibration, resulting in a more comfortable working environment.
3. Maintenance: These compressors require regular oil changes and maintenance to ensure the proper functioning of the lubrication system. The oil filter may need replacement, and the oil level should be regularly checked and topped up.
4. Applications: Oil-lubricated compressors are commonly used in applications that demand high air quality and continuous operation, such as industrial settings, workshops, and manufacturing facilities.
Oil-Free Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-free air compressors do not use oil for lubrication. Instead, they utilize alternative materials, such as specialized coatings, self-lubricating materials, or water-based lubricants, to reduce friction and wear.
2. Performance: Oil-free compressors generally have a higher airflow capacity, making them suitable for applications where a large volume of compressed air is required. However, they may produce slightly more noise and vibration compared to oil-lubricated compressors.
3. Maintenance: Oil-free compressors typically require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated ones. They do not need regular oil changes or oil filter replacements. However, it is still important to perform routine maintenance tasks such as air filter cleaning or replacement.
4. Applications: Oil-free compressors are commonly used in applications where air quality is crucial, such as medical and dental facilities, laboratories, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications. They are also favored for portable and consumer-grade compressors.
When selecting between oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors, consider the specific requirements of your application, including air quality, noise levels, maintenance needs, and expected usage. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and lubrication to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the air compressor.


editor by CX 2023-10-09
China 22kw 30HP Direct Drive Screw Air Compressors for Operating Condition Industry air compressor oil
Item Description
| ModelZ | SGD Series | ||||
| Kind of Cooling | Air Cooling/H2o cooling | ||||
| Motor Electrical power | kw/hp | 7.5~250kw(10~350hp) | |||
| Operating Force | Mpa | 0.8~1.2(customizable) | |||
| Starting up Mode | Y-Δ | ||||
| Type of Driving | Driect pushed | ||||
| Voltage | 380V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 220V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 440V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 415V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ Can be customized |
||||
| Exhaust Oil Volum | <3ppm | ||||
| Sounds | db | 68±2 | |||
| Outlet Air Humidity | ºC | ambient temperature+15ºC | |||
Technical Info of Immediate Travel Electric Motor Screw Air Compressors
| Model | Working Pressure | Capacity | Motor Electrical power | Driven Strategy | Cooling Approach | Dimension(mm) | Web Weight | Air Outlet Pipe Diameter | ||||
| Psi | bar | Cfm | m3/min | kw/hp | L | W | H | KGS | ||||
| SGD08 | 102 | seven | forty two.four | 1.2 | 7.5/10 | Direct Drive | Air Cooling / Drinking water Cooling |
900 | 670 | 850 | 200 | 1/2” |
| 116 | 8 | 38.eight | one.1 | |||||||||
| one hundred forty five | 10 | 33.five | .ninety five | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 28.three | .8 | |||||||||
| SGD11 | 102 | seven | 58.three | one.sixty five | 11/fifteen | 1080 | 750 | 1571 | 280 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | fifty three | one.5 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 45.nine | 1.three | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 38.eight | 1.1 | |||||||||
| SGD15 | 102 | seven | 88.3 | two.5 | 15/twenty | 1080 | 750 | 1571 | 300 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | eighty one.two | two.3 | |||||||||
| one hundred forty five | ten | seventy four.two | 2.1 | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 67.1 | 1.nine | |||||||||
| SGD18 | 102 | 7 | 113 | three.2 | 18.5/twenty five | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 430 | 1” | ||
| 116 | eight | a hundred and five.9 | 3 | |||||||||
| one hundred forty five | ten | 95.three | two.seven | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | eighty four.7 | 2.4 | |||||||||
| SGD22 | one hundred | seven | 134.two | 3.8 | 22/30 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 450 | 1” | ||
| 116 | eight | 127.one | 3.six | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 113 | three.two | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 95.three | two.7 | |||||||||
| SGD30 | 102 | 7 | 187.one | 5.three | 30/40 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 500 | 1” | ||
| 116 | eight | 176.6 | five | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 158.nine | four.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 141.2 | 4 | |||||||||
| SGD37 | 102 | seven | 240.one | six.8 | 37/fifty | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 650 | 11/2″ | ||
| 116 | eight | 218.nine | six.2 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 197.seven | 5.six | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 176.six | 5 | |||||||||
| SGD45 | 102 | 7 | 261.3 | seven.4 | 45/sixty | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 680 | 11/2″ | ||
| 116 | eight | 247.2 | seven | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | 10 | 218.9 | six.two | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 197.seven | five.six | |||||||||
| SGD55 | 102 | seven | 353.one | ten | 55/75 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1150 | 2″ | ||
| 116 | eight | 339 | nine.6 | |||||||||
| one hundred forty five | 10 | 300.one | eight.five | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 268.4 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| SGD75 | 102 | 7 | 473.two | thirteen.four | 75/100 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1200 | 2″ | ||
| 116 | eight | 444.nine | twelve.six | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | 10 | 395.5 | eleven.two | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 353.one | 10 | |||||||||
| SGD90 | 102 | 7 | 572 | sixteen.2 | 90/one hundred twenty | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1350 | 2″ | ||
| 116 | 8 | 529.7 | 15 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 487.3 | 13.8 | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 434.3 | 12.three | |||||||||
| SGD110 | 102 | seven | 741.five | 21 | 110/150 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1800 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | eight | 699.1 | 19.8 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 614.four | seventeen.four | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 522.six | 14.8 | |||||||||
| SGD132 | 102 | seven | 865.one | 24.5 | 132/one hundred seventy five | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1850 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | eight | 819.2 | 23.2 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | 10 | 723.nine | twenty.five | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 614.four | seventeen.four | |||||||||
| SGD160 | 102 | 7 | 1013.4 | 28.seven | 160/200 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 2000 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | eight | 974.6 | 27.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 868.six | 24.6 | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 759.2 | 21.5 | |||||||||
| SGD185 | 102 | seven | 1129.nine | 32 | 185/250 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3500 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1073.four | 30.four | |||||||||
| 145 | ten | 967.5 | 27.four | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 875.7 | 24.8 | |||||||||
| SGD220 | 102 | 7 | 1271.2 | 36 | 220/300 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3800 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1211.one | 34.3 | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 1066.four | 30.two | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 978.one | 27.7 | |||||||||
| SGD250 | 102 | seven | 1483 | 42 | 250/350 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 4000 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | eight | 1430.1 | forty.five | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1348.eight | 38.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 1218.2 | 34.5 | |||||||||
| SGD315 | 102 | 7 | 1800.eight | 51 | 315/430 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6000 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1772.six | 50.two | |||||||||
| a hundred forty five | ten | 1571.3 | forty four.five | |||||||||
| 174 | twelve | 1412.four | forty | |||||||||
| SGD355 | 102 | seven | 2259.eight | 64 | 355/480 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6500 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | eight | 2153.9 | 61 | |||||||||
| one hundred forty five | ten | 1995 | 56.five | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1730.2 | forty nine | |||||||||
Q1: What is the rotor pace for the air finish?
A1: 2980rmp.
Q2: What’s your lead time?
A2: usually, 5-7 days. (OEM orders: 15days)
Q3: Can you offer water cooled air compressor?
A3: Yes, we can (normally, air cooled type).
This autumn: What’s the payment term?
A4: T/T, L/C, Western Union, etc. Also we could accept USD, RMB, and other currency.
Q5: Do you accept customized voltage?
A5: Yes. 380V/50Hz/3ph, 380V/60Hz/3ph, 220V/50Hz/3ph, 220V/60Hz/3ph, 440V/50Hz/3ph, 440V/60Hz/3ph, or as per your requests.
Q6: What is your guarantee for air compressor?
A6: One year for the whole air compressor(not such as the consumption spare areas) and technical supports can be offered in accordance to your demands.
Q7: Can you accept OEM orders?
A7: Of course, OEM orders are warmly welcome.
Q8: How about your customer service and after-sales service?
A8: 24hrs on-line support, 48hrs problem solved promise.
Q9: Do you have spare parts in stock?
A9: Yes, we do.
Q10: What kind of initial lubrication oil you used in air compressor?
A10: TOTAL 46# mineral oil.
|
US $1,900-3,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 1920/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| ModelZ | SGD Series | ||||
| Type of Cooling | Air Cooling/Water cooling | ||||
| Motor Power | kw/hp | 7.5~250kw(10~350hp) | |||
| Working Pressure | Mpa | 0.8~1.2(customizable) | |||
| Starting Mode | Y-Δ | ||||
| Type of Driving | Driect driven | ||||
| Voltage | 380V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 220V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 440V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 415V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ Can be customized |
||||
| Exhaust Oil Volum | <3ppm | ||||
| Noise | db | 68±2 | |||
| Outlet Air Humidity | ºC | ambient temperature+15ºC | |||
###
| Model | Working Pressure | Capacity | Motor Power | Driven Method | Cooling Method | Dimension(mm) | Net Weight | Air Outlet Pipe Diameter | ||||
| Psi | bar | Cfm | m3/min | kw/hp | L | W | H | KGS | ||||
| SGD08 | 102 | 7 | 42.4 | 1.2 | 7.5/10 | Direct Drive | Air Cooling / Water Cooling |
900 | 670 | 850 | 200 | 1/2” |
| 116 | 8 | 38.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 33.5 | 0.95 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 28.3 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| SGD11 | 102 | 7 | 58.3 | 1.65 | 11/15 | 1080 | 750 | 1020 | 280 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 53 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 45.9 | 1.3 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 38.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| SGD15 | 102 | 7 | 88.3 | 2.5 | 15/20 | 1080 | 750 | 1020 | 300 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 81.2 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 74.2 | 2.1 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 67.1 | 1.9 | |||||||||
| SGD18 | 102 | 7 | 113 | 3.2 | 18.5/25 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 430 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 105.9 | 3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 95.3 | 2.7 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 84.7 | 2.4 | |||||||||
| SGD22 | 100 | 7 | 134.2 | 3.8 | 22/30 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 450 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 127.1 | 3.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 113 | 3.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 95.3 | 2.7 | |||||||||
| SGD30 | 102 | 7 | 187.1 | 5.3 | 30/40 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 500 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 176.6 | 5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 158.9 | 4.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 141.2 | 4 | |||||||||
| SGD37 | 102 | 7 | 240.1 | 6.8 | 37/50 | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 650 | 11/2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 218.9 | 6.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 197.7 | 5.6 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 176.6 | 5 | |||||||||
| SGD45 | 102 | 7 | 261.3 | 7.4 | 45/60 | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 680 | 11/2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 247.2 | 7 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 218.9 | 6.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 197.7 | 5.6 | |||||||||
| SGD55 | 102 | 7 | 353.1 | 10 | 55/75 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1150 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 339 | 9.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 300.1 | 8.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 268.4 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| SGD75 | 102 | 7 | 473.2 | 13.4 | 75/100 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1200 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 444.9 | 12.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 395.5 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 353.1 | 10 | |||||||||
| SGD90 | 102 | 7 | 572 | 16.2 | 90/120 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1350 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 529.7 | 15 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 487.3 | 13.8 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 434.3 | 12.3 | |||||||||
| SGD110 | 102 | 7 | 741.5 | 21 | 110/150 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1800 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 699.1 | 19.8 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 614.4 | 17.4 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 522.6 | 14.8 | |||||||||
| SGD132 | 102 | 7 | 865.1 | 24.5 | 132/175 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1850 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 819.2 | 23.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 723.9 | 20.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 614.4 | 17.4 | |||||||||
| SGD160 | 102 | 7 | 1013.4 | 28.7 | 160/200 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 2000 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 974.6 | 27.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 868.6 | 24.6 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 759.2 | 21.5 | |||||||||
| SGD185 | 102 | 7 | 1129.9 | 32 | 185/250 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3500 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1073.4 | 30.4 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 967.5 | 27.4 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 875.7 | 24.8 | |||||||||
| SGD220 | 102 | 7 | 1271.2 | 36 | 220/300 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3800 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1211.1 | 34.3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1066.4 | 30.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 978.1 | 27.7 | |||||||||
| SGD250 | 102 | 7 | 1483 | 42 | 250/350 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 4000 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1430.1 | 40.5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1348.8 | 38.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1218.2 | 34.5 | |||||||||
| SGD315 | 102 | 7 | 1800.8 | 51 | 315/430 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6000 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1772.6 | 50.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1571.3 | 44.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1412.4 | 40 | |||||||||
| SGD355 | 102 | 7 | 2259.8 | 64 | 355/480 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6500 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 2153.9 | 61 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1995 | 56.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1730.2 | 49 | |||||||||
|
US $1,900-3,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 1920/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| ModelZ | SGD Series | ||||
| Type of Cooling | Air Cooling/Water cooling | ||||
| Motor Power | kw/hp | 7.5~250kw(10~350hp) | |||
| Working Pressure | Mpa | 0.8~1.2(customizable) | |||
| Starting Mode | Y-Δ | ||||
| Type of Driving | Driect driven | ||||
| Voltage | 380V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 220V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 440V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ 415V / 3PH / 50HZ / 60HZ Can be customized |
||||
| Exhaust Oil Volum | <3ppm | ||||
| Noise | db | 68±2 | |||
| Outlet Air Humidity | ºC | ambient temperature+15ºC | |||
###
| Model | Working Pressure | Capacity | Motor Power | Driven Method | Cooling Method | Dimension(mm) | Net Weight | Air Outlet Pipe Diameter | ||||
| Psi | bar | Cfm | m3/min | kw/hp | L | W | H | KGS | ||||
| SGD08 | 102 | 7 | 42.4 | 1.2 | 7.5/10 | Direct Drive | Air Cooling / Water Cooling |
900 | 670 | 850 | 200 | 1/2” |
| 116 | 8 | 38.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 33.5 | 0.95 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 28.3 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| SGD11 | 102 | 7 | 58.3 | 1.65 | 11/15 | 1080 | 750 | 1020 | 280 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 53 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 45.9 | 1.3 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 38.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| SGD15 | 102 | 7 | 88.3 | 2.5 | 15/20 | 1080 | 750 | 1020 | 300 | 3/4” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 81.2 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 74.2 | 2.1 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 67.1 | 1.9 | |||||||||
| SGD18 | 102 | 7 | 113 | 3.2 | 18.5/25 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 430 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 105.9 | 3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 95.3 | 2.7 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 84.7 | 2.4 | |||||||||
| SGD22 | 100 | 7 | 134.2 | 3.8 | 22/30 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 450 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 127.1 | 3.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 113 | 3.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 95.3 | 2.7 | |||||||||
| SGD30 | 102 | 7 | 187.1 | 5.3 | 30/40 | 1380 | 850 | 1185 | 500 | 1” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 176.6 | 5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 158.9 | 4.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 141.2 | 4 | |||||||||
| SGD37 | 102 | 7 | 240.1 | 6.8 | 37/50 | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 650 | 11/2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 218.9 | 6.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 197.7 | 5.6 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 176.6 | 5 | |||||||||
| SGD45 | 102 | 7 | 261.3 | 7.4 | 45/60 | 1500 | 1000 | 1345 | 680 | 11/2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 247.2 | 7 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 218.9 | 6.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 197.7 | 5.6 | |||||||||
| SGD55 | 102 | 7 | 353.1 | 10 | 55/75 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1150 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 339 | 9.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 300.1 | 8.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 268.4 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| SGD75 | 102 | 7 | 473.2 | 13.4 | 75/100 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1200 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 444.9 | 12.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 395.5 | 11.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 353.1 | 10 | |||||||||
| SGD90 | 102 | 7 | 572 | 16.2 | 90/120 | 1800 | 1250 | 1670 | 1350 | 2" | ||
| 116 | 8 | 529.7 | 15 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 487.3 | 13.8 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 434.3 | 12.3 | |||||||||
| SGD110 | 102 | 7 | 741.5 | 21 | 110/150 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1800 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 699.1 | 19.8 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 614.4 | 17.4 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 522.6 | 14.8 | |||||||||
| SGD132 | 102 | 7 | 865.1 | 24.5 | 132/175 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 1850 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 819.2 | 23.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 723.9 | 20.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 614.4 | 17.4 | |||||||||
| SGD160 | 102 | 7 | 1013.4 | 28.7 | 160/200 | 2300 | 1470 | 1840 | 2000 | 2 1/2” | ||
| 116 | 8 | 974.6 | 27.6 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 868.6 | 24.6 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 759.2 | 21.5 | |||||||||
| SGD185 | 102 | 7 | 1129.9 | 32 | 185/250 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3500 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1073.4 | 30.4 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 967.5 | 27.4 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 875.7 | 24.8 | |||||||||
| SGD220 | 102 | 7 | 1271.2 | 36 | 220/300 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 3800 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1211.1 | 34.3 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1066.4 | 30.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 978.1 | 27.7 | |||||||||
| SGD250 | 102 | 7 | 1483 | 42 | 250/350 | 3150 | 1980 | 2152 | 4000 | DN85 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1430.1 | 40.5 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1348.8 | 38.2 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1218.2 | 34.5 | |||||||||
| SGD315 | 102 | 7 | 1800.8 | 51 | 315/430 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6000 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 1772.6 | 50.2 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1571.3 | 44.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1412.4 | 40 | |||||||||
| SGD355 | 102 | 7 | 2259.8 | 64 | 355/480 | 4000 | 1980 | 2152 | 6500 | DN110 | ||
| 116 | 8 | 2153.9 | 61 | |||||||||
| 145 | 10 | 1995 | 56.5 | |||||||||
| 174 | 12 | 1730.2 | 49 | |||||||||
Choosing the Right Air Compressor For Your Home
You will find that air compressors are indispensable tools for a variety of situations, including garages, home workshops, and basements. These tools can power a variety of tools, and each model is sized to suit the job at hand. Because air compressors have only one motor, they are lightweight, compact, and easy to handle. Using one air compressor to power several tools will also reduce the wear and tear on individual components. This article will introduce some important characteristics to look for when choosing the right air compressor for your home.
Positive displacement
A positive displacement compressor applies pressure to a fluid, whereas a centrifugal one does the opposite. A positive displacement compressor creates the desired pressure by trapping air and increasing its volume. Its discharge valve releases the high-pressure gas. These compressors are used in industrial applications and nuclear power plants. The difference between a positive and negative displacement compressor is that a positive displacement compressor can compress and release air at a consistent rate.
A positive displacement air compressor uses a reciprocating piston to compress air. This reduces the volume of the air in the compression chamber, and a discharge valve opens when the pressure reaches the desired level. These compressors are used in bicycle pumps and other pneumatic tools. Positive displacement air compressors have multiple inlet ports and have several configurations. Positive displacement air compressors have a single-acting and double-acting piston, and can be oil-lubricated or oil-free.
A positive displacement air compressor is different from a dynamic compressor. It draws air into the compression chambers and then releases the pressure when the valve is opened. Positive displacement compressors are common in industrial applications and are available in single-acting, double-acting, and oil-lubricated models. Large piston compressors have ventilated intermediate pieces and crossheads on gudgeon pins. Smaller models have permanently sealed crankcases with bearings.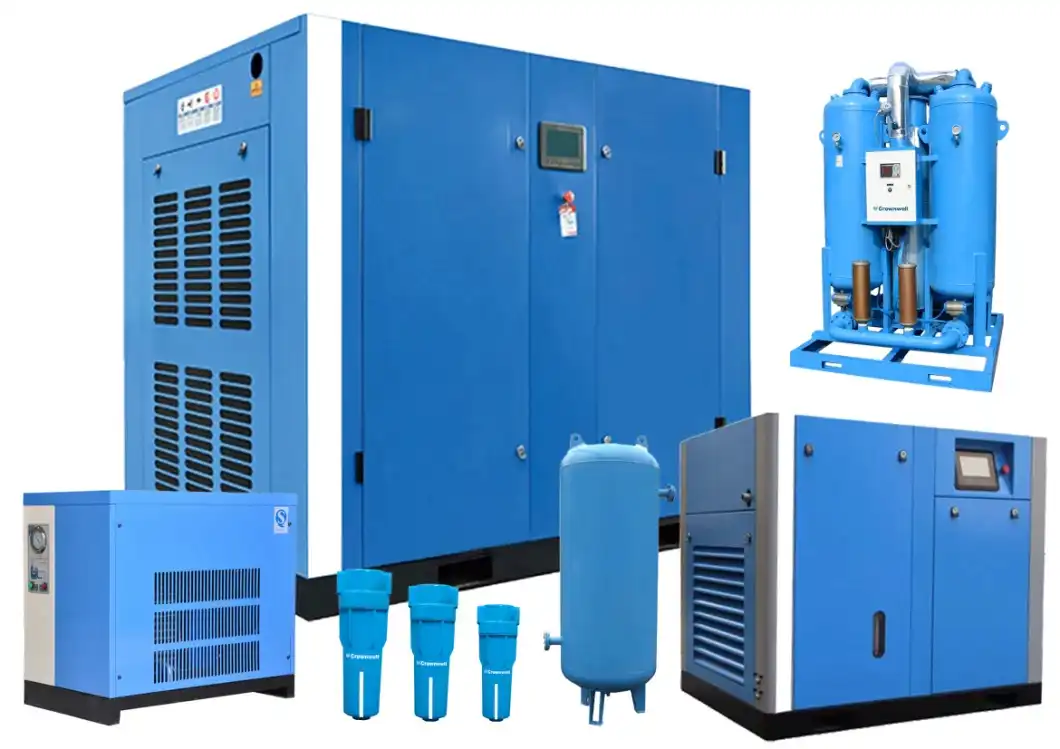
Oil-free
Oil-free air compressors have some advantages over their oil-lubricated counterparts. They do not require lubrication oil because they are coated with Teflon. The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction and is layered, so it slides past other layers with little effort. Because of this, oil-free compressors tend to be cheaper and still deliver comparable performance. Oil-free compressors are a good choice for industrial applications.
The life of an oil-free air compressor is significantly longer than an oil-lubricated counterpart. These models can operate up to 2,000 hours, four times longer than the average oil-lubed compressor. Oil-free compressors also have a significantly lower operating noise than their oil-lubricated counterparts. And because they don’t need oil changes, they are quieter. Some even last up to 2,000 hours.
An oil-free air compressor is a good choice if your application requires high levels of purity. Several applications require ultra-pure air, and even a drop of oil can cause product spoilage or damage to production equipment. In addition to the health risks, an oil-free air compressor reduces the costs associated with oil contamination and minimizes leaks. It also eliminates the need for oil collection, disposal, and treatment.
A typical oil-free air compressor is very efficient, requiring only about 18% of the full load horsepower. However, oil-free compressors have a higher risk of premature failure and are not recommended for large-scale industrial applications. They may also use up to 18% of the compressor’s full capacity. They may sound appealing, but you must make sure you understand the benefits of an oil-free air compressor before choosing one for your industrial applications.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor is designed to provide the power for a single pneumatic tool or device. These machines are generally smaller than two-stage compressors and produce less heat and energy. These machines aren’t designed for heavy-duty industries, but they are still highly effective for a variety of applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing plants. They can also be used in borewells, as they are suitable for small spaces with low air flow requirements.
A single-stage air compressor has one cylinder and two valves – the inlet and the delivery valves. Both of these valves function mechanically, with the inlet valve controlling torque and the delivery one controlling air pressure. Generally, single-stage compressors are powered by a gas engine, but there are also electric models available. The single-stage air compressor is the most common type of air compressor. It has a single cylinder, one piston, and one air cylinder.
The single-stage air compressors are used for small projects or personal use. A two-stage air compressor is more effective for industrial projects. Its longer air end life makes it more efficient. It is also more efficient for use in the automotive industry, where the engine has many cylinders. In general, single-stage compressors require a higher power level. The single-stage model is ideal for small projects, while a two-stage one is suitable for larger-scale arsenals.
CFM
The cubic foot-per-minute (CFM) of an air compressor is the output of the machine. In order to calculate the CFM level, start by looking at the compressor’s specifications. You should know how many cubic feet the unit can hold and how many pounds per square inch it can compress. Once you have these information, you can calculate the CFM. Now you can use these numbers to select an appropriate air compressor for your needs.
The most common way to increase the CFM of an air compressor is to turn the regulator down. By turning the dial down, the air compressor will produce more than 10 CFM. You can also try connecting two output valves. Make sure that the settings are adjusted properly before you begin. This will ensure that your air compressor is functioning at its maximum efficiency and lifespan. To increase the CFM of your air compressor, first check that your regulator is calibrated for the desired pressure level.
To calculate the CFM of an air compressor, first determine the tank volume of the machine. Then, multiply this volume by the time it takes to fill the tank. Then, divide the result by 60 seconds to calculate the CFM. Once you know how much air your machine can hold, you can choose a suitable air compressor. If you’re working in a confined area, you should buy a tool with a large tank.
PSI
The PSI of an air compressor is the pressure that it can output. A typical air compressor has a gauge connected to the airline at the bottom, next to it, or between the two. The gauge tells the actual pressure of the air compressor, while the cut-out pressure is determined by the manufacturer. The manufacturer recommends that you set the cut-out pressure twenty to forty PSI higher than the factory recommended pressure. If you want to set the pressure for your nail gun, you can use the cut-in and cut-out pressures on your compressor, and the tank won’t exceed this range.
The PSI of an air compressor measures the force that it can deliver, which is often in pounds per square inch. For most air tools, you need at least forty to 90 psi. In general, reciprocating air compressors work on an on/off basis. This relationship is known as the duty cycle. All air compressors are rated for a particular duty cycle, such as fifty percent on and twenty-five percent off.
The Psig of an air compressor is not free, as many people believe. The PSI of an air compressor is not free, but it is essential to maintain it for safe operations. If you’re having trouble maintaining a consistent pressure, consider turning down the PSI of your compressor by 2 psig. This will determine the critical pressure for the machine. You’ll also increase the amount of energy in the system by one percent.
Power source
The power source for an air compressor is crucial in its operation. Without the correct voltage and amperage, air compressors will not function properly. The power source must be close to the compressor so that it can plug into an electrical outlet. If it is too far from the outlet, the compressor may not be able to build enough pressure. When this happens, the fuse inside the air compressor will turn off to protect the user. The power source should be a safe distance from the compressor.
Most manufacturers do not specify the power source for an air compressor. Depending on the horsepower, the compressor will require approximately four amps of power. A one-horsepower compressor would draw about twelve amps. If it were powered by a typical 120-volt household supply, its motor would exceed the 15-amp breaker capacity. A larger air compressor, however, will require a separate 15-amp power source, making it impossible to use it with this type of power source.
The power source for an air compressor is typically electrical alternating current (AC) that is equivalent to the voltage on a standard wall outlet. A three-phase air compressor, on the other hand, requires a special AC supply with three electrical offset pulses. Regardless of the type of air compressor, the power source must be compatible with the incoming power service. One of the most common problems when attempting to connect an air compressor to an AC power source is undersized wire. This results in low voltage and high amperes, tripping of over-load relays and blown fuses.


editor by czh 2023-01-04