Product Description
| Product Name | Oil-Free Booster Compressor |
| Model No | BW-3/5/10/15/20/30… |
| Inlet Pressure | 0.4Mpa( G ) |
| Exhaust Pressure | 150/200Mpa( G ) |
| Type | High Pressure Oil Free |
| Accessories | Filling Manifold, Piston ring, Etc |
| Oilless High Pressure O2 Compressor Specification | |||||
| NO | Volume | Inlet pressure | Outlet pressure | Type | Cooling type |
| 1 | 1-3m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Wind |
| 2 | 4-12m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Wind |
| 3 | 13-40m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 3 lines 3 stages W type | Water |
| 4 | 13-60m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Water |
| 5 | 40-80m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 4 lines 4 stages S type | Water |
| 6 | 80-120m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 4 lines 4 stages S type | Water |
If you have compressor inquiry please tell us follows information when you send inquiry:
*Compressor working medium: If single gas ,how many purity ? if mixed gas , what’s gas content lit ?
*Suction pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Exhaust pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Flow rate per hour for compressor: _____Nm³/h
Compressor gas suction temperature:_____ºC
Compressor working hours per day :_____hours
Compressor working site altitude :_____m
Environment temperature : _____ºC
Has cooling water in the site or not ?______
Voltage and frequency for 3 phase :____________
Do not has water vapor or H2S in the gas ?______
Application for compressor?__________
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Product Name: | Oxygen,Nitrogen Compressor |
| Gas Type: | Oxygen,Nitrogen,Special Gas |
| Cooling Method: | Air Cooling Water Cooling |
| Application: | Filling Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How Do You Maintain a Gas Air Compressor?
Maintaining a gas air compressor is essential to ensure its optimal performance, longevity, and safe operation. Regular maintenance helps prevent breakdowns, extends the compressor’s lifespan, and promotes efficient operation. Here are some key maintenance steps for a gas air compressor:
1. Read the Manual:
Before performing any maintenance tasks, thoroughly read the manufacturer’s manual specific to your gas air compressor model. The manual provides important instructions and guidelines for maintenance procedures, including recommended intervals and specific maintenance requirements.
2. Check and Change the Oil:
Gas air compressors typically require regular oil changes to maintain proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear. Check the oil level regularly and change it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Use the recommended grade of oil suitable for your compressor model.
3. Inspect and Replace Air Filters:
Inspect the air filters regularly and clean or replace them as needed. Air filters prevent dust, debris, and contaminants from entering the compressor’s internal components. Clogged or dirty filters can restrict airflow and reduce performance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for filter cleaning or replacement.
4. Drain Moisture from the Tank:
Gas air compressors accumulate moisture in the compressed air, which can lead to corrosion and damage to the tank and internal components. Drain the moisture from the tank regularly to prevent excessive moisture buildup. Refer to the manual for instructions on how to properly drain the moisture.
5. Check and Tighten Connections:
Regularly inspect all connections, fittings, and hoses for any signs of leaks or loose connections. Tighten any loose fittings and repair or replace damaged hoses or connectors. Leaks can lead to reduced performance and inefficiency.
6. Inspect Belts and Pulleys:
If your gas air compressor has belts and pulleys, inspect them for wear, tension, and proper alignment. Replace any worn or damaged belts and ensure proper tension to maintain optimal performance.
7. Clean the Exterior and Cooling Fins:
Keep the exterior of the gas air compressor clean from dirt, dust, and debris. Use a soft cloth or brush to clean the surfaces. Additionally, clean the cooling fins regularly to remove any accumulated debris that can impede airflow and cause overheating.
8. Schedule Professional Servicing:
While regular maintenance can be performed by the user, it is also important to schedule professional servicing at recommended intervals. Professional technicians can perform thorough inspections, conduct more complex maintenance tasks, and identify any potential issues that may require attention.
9. Follow Safety Precautions:
When performing maintenance tasks on a gas air compressor, always follow safety precautions outlined in the manual. This may include wearing protective gear, disconnecting the power source, and ensuring proper ventilation in confined spaces.
By following these maintenance steps and adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines, you can keep your gas air compressor in optimal condition, prolong its lifespan, and ensure safe and efficient operation.
.webp)
What Is the Impact of Altitude on Gas Air Compressor Performance?
Altitude can have a significant impact on the performance of gas air compressors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Decreased Air Density:
As altitude increases, the air density decreases. This reduction in air density affects the performance of gas air compressors, primarily because compressors rely on the intake of ambient air to generate compressed air. With lower air density at higher altitudes, the compressor’s ability to draw in a sufficient volume of air is reduced.
2. Reduced Compressor Output:
The decrease in air density directly affects the compressor’s output. Gas air compressors may experience a decrease in their maximum airflow and pressure capabilities at higher altitudes. This reduction in output can impact the compressor’s efficiency and its ability to deliver the required compressed air for various applications.
3. Increased Compressor Workload:
At higher altitudes, gas air compressors need to work harder to maintain the desired level of compressed air output. The reduced air density means the compressor must compress a larger volume of air to achieve the same pressure as it would at lower altitudes. This increased workload can lead to higher energy consumption, increased wear and tear on the compressor components, and potentially decreased overall performance and lifespan.
4. Engine Power Loss:
If the gas air compressor is powered by an internal combustion engine (such as gasoline or diesel), altitude can also impact the engine’s performance. As the air density decreases, the engine may experience a power loss due to reduced oxygen availability for combustion. This can result in reduced engine horsepower and torque, affecting the compressor’s ability to generate compressed air.
5. Considerations for Proper Sizing:
When selecting a gas air compressor for use at higher altitudes, it is crucial to consider the specific altitude conditions and adjust the compressor’s size and capacity accordingly. Choosing a compressor with a higher airflow and pressure rating than required at sea level can help compensate for the reduced performance at higher altitudes.
6. Maintenance and Adjustments:
Regular maintenance and adjustments are necessary to optimize the performance of gas air compressors operating at higher altitudes. This includes monitoring and adjusting the compressor’s intake systems, fuel-to-air ratio, and ignition timing to account for the reduced air density and maintain proper combustion efficiency.
In summary, altitude has a notable impact on the performance of gas air compressors. The decrease in air density at higher altitudes leads to reduced compressor output, increased compressor workload, potential engine power loss, and considerations for proper sizing and maintenance. Understanding these effects is crucial for selecting and operating gas air compressors effectively in various altitude conditions.
.webp)
How Do You Choose the Right Size Gas Air Compressor for Your Needs?
Choosing the right size gas air compressor is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency for your specific needs. Selecting a compressor that is too small may result in insufficient airflow or pressure, while choosing one that is too large can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and higher costs. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors to consider when choosing the right size gas air compressor:
1. Required Airflow:
Determine the airflow requirements of your applications. Consider the tools, equipment, or processes that will be powered by the compressor and their respective airflow demands. The required airflow is typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Determine the total CFM required, taking into account any simultaneous or intermittent tool usage.
2. Operating Pressure:
Identify the operating pressure required for your applications. Different tools and systems have specific pressure requirements, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Ensure that the compressor you choose can deliver the required pressure consistently.
3. Duty Cycle:
Consider the duty cycle, which refers to the amount of time the compressor will be in operation within a given period. Some applications may require continuous operation, while others involve intermittent or occasional use. Take into account the duty cycle to ensure that the compressor can handle the expected workload without overheating or experiencing excessive wear.
4. Tank Size:
The tank size of a gas air compressor determines its ability to store compressed air and provide a steady supply. A larger tank can help accommodate fluctuations in demand and reduce the frequency of the compressor cycling on and off. Consider the required storage capacity based on the specific applications and the desired balance between continuous operation and storage capacity.
5. Power Source:
Gas air compressors can be powered by different fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. Consider the availability and cost of the fuel options in your location, as well as the specific requirements of your applications. Choose a compressor that is compatible with a power source that suits your needs.
6. Portability:
Determine if portability is a requirement for your applications. If you need to move the compressor to different job sites or locations, consider a portable model with features like wheels, handles, or a compact design that facilitates easy transportation.
7. Noise Level:
If noise is a concern in your working environment, consider the noise level of the compressor. Gas air compressors can vary in their noise output, and certain models may have noise-reducing features or insulation to minimize sound emissions.
8. Manufacturer Recommendations:
Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for selecting the appropriate compressor size for your specific needs. Manufacturers often provide guidelines based on the anticipated applications, airflow requirements, and other factors to help you make an informed decision.
By considering these factors and carefully assessing your specific requirements, you can choose the right size gas air compressor that meets your airflow, pressure, duty cycle, and other operational needs. It’s advisable to consult with industry professionals or compressor experts for guidance, especially for complex or specialized applications.


editor by CX 2023-11-07
China Good quality Lead The Industry CHINAMFG Supplier Medical Oxygen Compressor arb air compressor
Product Description
| Product Name | Oil-Free Booster Compressor |
| Model No | BW-3/5/10/15/20/30… |
| Inlet Pressure | 0.4Mpa( G ) |
| Exhaust Pressure | 150/200Mpa( G ) |
| Type | High Pressure Oil Free |
| Accessories | Filling Manifold, Piston ring, Etc |
| Oilless High Pressure O2 Compressor Specification | |||||
| NO | Volume | Inlet pressure | Outlet pressure | Type | Cooling type |
| 1 | 1-3m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Wind |
| 2 | 4-12m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Wind |
| 3 | 13-40m³ | 0.3-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 3 lines 3 stages W type | Water |
| 4 | 13-60m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 2 lines 4 stages vertical type | Water |
| 5 | 40-80m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 4 lines 4 stages S type | Water |
| 6 | 80-120m³ | 0.2-0.4MPa | 15MPa | 4 lines 4 stages S type | Water |
If you have compressor inquiry please tell us follows information when you send inquiry:
*Compressor working medium: If single gas ,how many purity ? if mixed gas , what’s gas content lit ?
*Suction pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Exhaust pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Flow rate per hour for compressor: _____Nm³/h
Compressor gas suction temperature:_____ºC
Compressor working hours per day :_____hours
Compressor working site altitude :_____m
Environment temperature : _____ºC
Has cooling water in the site or not ?______
Voltage and frequency for 3 phase :____________
Do not has water vapor or H2S in the gas ?______
Application for compressor?__________
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Product Name: | Oxygen,Nitrogen Compressor |
| Gas Type: | Oxygen,Nitrogen,Special Gas |
| Cooling Method: | Air Cooling Water Cooling |
| Application: | Filling Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
What Is the Fuel Efficiency of Gas Air Compressors?
The fuel efficiency of gas air compressors can vary depending on several factors, including the compressor’s design, engine size, load capacity, and usage patterns. Gas air compressors typically use internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or propane to generate the mechanical energy required for compressing air. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can influence the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors:
1. Engine Design and Size:
The design and size of the engine in a gas air compressor can impact its fuel efficiency. Engines with advanced technologies such as fuel injection and electronic controls tend to offer better fuel efficiency compared to older carbureted engines. Additionally, larger engines may consume more fuel to produce the required power, resulting in lower fuel efficiency compared to smaller engines for the same workload.
2. Load Capacity and Usage Patterns:
The load capacity and usage patterns of the gas air compressor play a significant role in fuel efficiency. Compressors operating at or near their maximum load capacity for extended periods may consume more fuel compared to compressors operating at lower loads. Additionally, compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks may have better fuel efficiency due to reduced demand on the engine.
3. Maintenance and Tuning:
Proper maintenance and tuning of the gas air compressor’s engine can improve fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance tasks such as oil changes, air filter cleaning/replacement, spark plug inspection, and tuning the engine to the manufacturer’s specifications can help ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
4. Operating Conditions:
The operating conditions, including ambient temperature, altitude, and humidity, can affect the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors. Extreme temperatures or high altitudes may require the engine to work harder, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Additionally, operating in humid conditions can affect the combustion process and potentially impact fuel efficiency.
5. Fuel Type:
The type of fuel used in the gas air compressor can influence its fuel efficiency. Gasoline and propane are common fuel choices for gas air compressors. The energy content and combustion characteristics of each fuel can affect the amount of fuel consumed per unit of work done. It is important to consider the specific fuel requirements and recommendations of the compressor manufacturer for optimal fuel efficiency.
6. Operator Skills and Practices:
The skills and practices of the operator can also impact fuel efficiency. Proper operation techniques, such as avoiding excessive idling, maintaining consistent engine speeds, and minimizing unnecessary load cycles, can contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
It is important to note that specific fuel efficiency ratings for gas air compressors can vary widely depending on the aforementioned factors. Manufacturers may provide estimated fuel consumption rates or fuel efficiency data for their specific compressor models, which can serve as a reference point when comparing different models or making purchasing decisions.
Ultimately, to maximize fuel efficiency, it is recommended to select a gas air compressor that suits the intended application, perform regular maintenance, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, and operate the compressor efficiently based on the workload and conditions.
.webp)
How Do Gas Air Compressors Contribute to Energy Savings?
Gas air compressors can contribute to energy savings in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Efficient Power Source:
Gas air compressors are often powered by gasoline or diesel engines. Compared to electric compressors, gas-powered compressors can provide higher power output for a given size, resulting in more efficient compression of air. This efficiency can lead to energy savings, especially in applications where a significant amount of compressed air is required.
2. Reduced Electricity Consumption:
Gas air compressors, as standalone units that don’t rely on electrical power, can help reduce electricity consumption. In situations where the availability of electricity is limited or expensive, using gas air compressors can be a cost-effective alternative. By utilizing fuel-based power sources, gas air compressors can operate independently from the electrical grid and reduce dependence on electricity.
3. Demand-Sensitive Operation:
Gas air compressors can be designed to operate on demand, meaning they start and stop automatically based on the air requirements. This feature helps prevent unnecessary energy consumption during periods of low or no compressed air demand. By avoiding continuous operation, gas air compressors can optimize energy usage and contribute to energy savings.
4. Energy Recovery:
Some gas air compressors are equipped with energy recovery systems. These systems capture and utilize the heat generated during the compression process, which would otherwise be wasted. The recovered heat can be redirected and used for various purposes, such as space heating, water heating, or preheating compressed air. This energy recovery capability improves overall energy efficiency and reduces energy waste.
5. Proper Sizing and System Design:
Selecting the appropriate size and capacity of a gas air compressor is crucial for energy savings. Over-sizing a compressor can lead to excessive energy consumption, while under-sizing can result in inefficient operation and increased energy usage. Properly sizing the compressor based on the specific air demands ensures optimal efficiency and energy savings.
6. Regular Maintenance:
Maintaining gas air compressors in good working condition is essential for energy efficiency. Regular maintenance, including cleaning or replacing air filters, checking and repairing leaks, and ensuring proper lubrication, helps optimize compressor performance. Well-maintained compressors operate more efficiently, consume less energy, and contribute to energy savings.
7. System Optimization:
For larger compressed air systems that involve multiple compressors, implementing system optimization strategies can further enhance energy savings. This may include employing advanced control systems, such as variable speed drives or sequencers, to match compressed air supply with demand, minimizing unnecessary energy usage.
In summary, gas air compressors contribute to energy savings through their efficient power sources, reduced electricity consumption, demand-sensitive operation, energy recovery systems, proper sizing and system design, regular maintenance, and system optimization measures. By utilizing gas-powered compressors and implementing energy-efficient practices, businesses and industries can achieve significant energy savings in their compressed air systems.
.webp)
How Does a Gas Air Compressor Work?
A gas air compressor works by utilizing a gas engine to power a compressor pump, which draws in air and compresses it to a higher pressure. The compressed air can then be used for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a gas air compressor operates:
1. Gas Engine:
A gas air compressor is equipped with a gas engine as its power source. The gas engine is typically fueled by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. When the engine is started, the fuel is combusted within the engine’s cylinders, generating mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion.
2. Compressor Pump:
The gas engine drives the compressor pump through a mechanical linkage, such as a belt or direct coupling. The compressor pump is responsible for drawing in atmospheric air and compressing it to a higher pressure. There are different types of compressor pumps used in gas air compressors, including reciprocating, rotary screw, or centrifugal, each with its own operating principles.
3. Intake Stroke:
In a reciprocating compressor pump, the intake stroke begins when the piston moves downward within the cylinder. This creates a vacuum, causing the inlet valve to open and atmospheric air to be drawn into the cylinder. In rotary screw or centrifugal compressors, air is continuously drawn in through the intake port as the compressor operates.
4. Compression Stroke:
During the compression stroke in a reciprocating compressor, the piston moves upward, reducing the volume within the cylinder. This compression action causes the air to be compressed and its pressure to increase. In rotary screw compressors, two interlocking screws rotate, trapping and compressing the air between them. In centrifugal compressors, air is accelerated and compressed by high-speed rotating impellers.
5. Discharge Stroke:
Once the air is compressed, the discharge stroke begins in reciprocating compressors. The piston moves upward, further reducing the volume and forcing the compressed air out of the cylinder through the discharge valve. In rotary screw compressors, the compressed air is discharged through an outlet port as the interlocking screws continue to rotate. In centrifugal compressors, the high-pressure air is discharged from the impeller into the surrounding volute casing.
6. Pressure Regulation:
Gas air compressors often include pressure regulation mechanisms to control the output pressure of the compressed air. This can be achieved through pressure switches, regulators, or control systems that adjust the compressor’s operation based on the desired pressure setting. These mechanisms help maintain a consistent and controlled supply of compressed air for the specific application requirements.
7. Storage and Application:
The compressed air produced by the gas air compressor is typically stored in a receiver tank or used directly for applications. The receiver tank helps stabilize the pressure and provides a reservoir of compressed air for immediate use. From the receiver tank, the compressed air can be distributed through pipelines to pneumatic tools, machinery, or other devices that require the compressed air for operation.
Overall, a gas air compressor operates by using a gas engine to power a compressor pump, which draws in air and compresses it to a higher pressure. The compressed air is then regulated and used for various applications, providing a reliable source of power for pneumatic tools, machinery, and other equipment.


editor by CX 2023-11-03
China high quality Dw-3.1/15-52 Natural Gas Compressor Air or Water Cooled Piston Compressors Are Designed and Manufactured in Strictaccordance with Apl and ISO Standards arb air compressor
Product Description
HangZhou United Compressor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. was established in 2002 and is a high-tech enterprise in ZheJiang Province. The company has complete production equipment testing methods, and relies on its technological advantages to introduce, absorb, and digest new technologies and processes from abroad. The products have covered all domestic demand industries and regions, and are exported to multiple countries such as Russia, Tajikistan, India, Pakistan, North Korea, etc. It is a qualified supplier and partner for many domestic and foreign enterprises.
The company has a sales and service team that continuously provides customers with various energy-saving and modern compressor system products. In the past 10 years, the company has maintained rapid and stable development, providing products and services for industries such as natural gas, steel, petroleum, chemical, coal, mining, and metallurgy. We not only have mature products, but also have a capable after-sales service team, such as conducting pre-sales inspections of compressors, timely tracking during sales, and 24-hour after-sales repair and maintenance services.
Product Application
Mainly used for pressurized transmission of natural gas into the pipeline network (Natural pipeline gas extraction and combustible gas recovery tank filling)
It can also be used for stirring in the pharmaceutical and brewing industries, pressurized gas transportation in the chemical industry, blow molding bottle making in the food industry, and dust removal of parts in the machine manufacturing industry.
Product Features
1. This series of compressors is an advanced piston compressor unit produced and manufactured using the product technology of Mannes Mandermarg Company in Germany.
2. The product has the characteristics of low noise, low vibration, compact structure, smooth operation, safety and reliability, and high automation level. It can also be configured with a data-driven remote display and control system according to customer requirements.
3. Equipped with alarm and shutdown functions for low oil pressure, low water pressure, high temperature, low inlet pressure, and high exhaust pressure of the compressor, making the operation of the compressor more reliable.
Structure Introduction
The unit consists of a compressor host, electric motor, coupling, flywheel, pipeline system, cooling system, electrical equipment, and auxiliary equipment.
Reference Technical parameters and specifications
| NO. | MODEL | Compressed medium | Flow rate Nm³/h |
Inlet pressure MPa |
Outlet pressure MPa |
Rotating speed r/min |
Motor power KW |
Cooling mode | Overall dimension mm |
Weight Kg |
| 1 | DW-14/(0-0.2)-25 | Raw gas | 800 | 0-0.02 | 2.5 | 740 | 160 | Water cooled | 4800*3200*1915 | ~10000 |
| 2 | VW-8/18 | Vinylidene fluoride gas | 418 | Atmospheric pressure | 1.8 | 980 | 75 | Water cooled | 3700*2000*1700 | ~4500 |
| 3 | VWD-3.2/(0-0.2)-40 | Biogas | 230 | 0-0.2 | 4.0 | 740 | 45 | Water cooled | 6000*2500*2650 | ~8000 |
| 4 | VW-9/6 | Ethyl chloride gas | 470 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.6 | 980 | 55 | Water cooled | 2800*1720*1700 | ~3500 |
| 5 | DWF-12.4/(9-12)-14 | Carbon dioxide | 6400 | 0.9-1.2 | 1.4 | 740 | 185 | Air cooled | 6000*2700*2200 | ~10000 |
| 6 | VWF-2.86/5-16 | Nitrogen gas | 895 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 740 | 55 | Air cooled | 3200*2200*1750 | ~3500 |
| 7 | DW-2.4/(18-25)-50 | Raw gas | 2900 | 1.8-2.5 | 5.0 | 980 | 160 | Water cooled | 4300*3000*1540 | ~4500 |
| 8 | VW-5.6/(0-6)-6 | Isobutylene gas | 1650 | 0-0.6 | 0.6 | 740 | 45 | Water cooled | 2900X1900X1600 | ~3500 |
| 9 | VW-3.8/3.5 | Mixed gas | 200 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.35 | 980 | 18.5 | Water cooled | 2200*1945*1600 | ~2000 |
| 10 | ZW-1.7/3.5 | Vinyl chloride gas | 100 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.35 | 740 | 15 | Water cooled | 2700X1600X2068 | ~2000 |
| 11 | ZWF-0.96/5 | Hydrogen chloride gas | 55 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.5 | 740 | 11 | Air cooled | 2000*1500*2000 | ~1000 |
| 12 | VW-0.85/(0-14)-40 | Refrigerant gas | 300 | 0-1.4 | 4.0 | 740 | 55 | Water cooled | 4500*2300*1780 | ~5500 |
| 13 | DW-3.78/(8-13)-(16-24) | Ammonia gas | 2700 | 0.8-1.3 | 1.6-2.4 | 740 | 75 | Water cooled | 3200*2000*1700 | ~3500 |
Related products
| Warranty: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Lubrication Style: | Customized |
| Cooling System: | Air/Water /Mixed Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Customized |
| Structure Type: | Open Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Is the Typical Lifespan of a Gas Air Compressor?
The typical lifespan of a gas air compressor can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the compressor, its usage patterns, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. However, with proper care and maintenance, a gas air compressor can last for many years. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can affect the lifespan of a gas air compressor:
1. Quality of the Compressor:
The quality and construction of the gas air compressor play a significant role in determining its lifespan. Compressors made with high-quality materials, precision engineering, and robust components are generally more durable and can withstand heavy usage over an extended period.
2. Usage Patterns:
The usage patterns of the gas air compressor can impact its lifespan. If the compressor is used consistently and for extended periods, it may experience more wear and tear compared to compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks. Heavy-duty applications, such as continuous operation with high-demand tools, can put more strain on the compressor and potentially reduce its lifespan.
3. Maintenance Practices:
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, performing routine tasks like oil changes, filter cleaning/replacement, and inspection of components can help prevent issues and ensure optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and potential breakdowns.
4. Environmental Conditions:
The operating environment can significantly impact the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, presence of dust or debris, and exposure to corrosive substances can affect the compressor’s components and overall performance. Compressors used in harsh environments may require additional protection or specialized maintenance to mitigate these adverse conditions.
5. Proper Installation and Operation:
Proper installation and correct operation of the gas air compressor are essential for its longevity. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring proper ventilation, maintaining correct oil levels, and operating within the compressor’s specified capacity and pressure limits can help prevent excessive strain and premature wear.
Considering these factors, a well-maintained gas air compressor can typically last anywhere from 10 to 15 years or even longer. However, it’s important to note that this is a general estimate, and individual results may vary. Some compressors may experience shorter lifespans due to heavy usage, inadequate maintenance, or other factors, while others may last well beyond the expected lifespan with proper care and favorable conditions.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality gas air compressor, adhering to recommended maintenance practices, and using it within its intended capabilities can help maximize its lifespan and ensure reliable performance for an extended period.
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
What Are the Advantages of Using a Gas Air Compressor Over an Electric One?
Using a gas air compressor offers several advantages over an electric air compressor. Gas-powered compressors provide unique benefits in terms of mobility, versatility, power, and convenience. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using a gas air compressor:
1. Portability and Mobility:
Gas air compressors are typically more portable and mobile compared to electric compressors. They often feature handles, wheels, or trailers, allowing for easy transportation to different locations. This portability is especially advantageous in situations where compressed air is needed at remote job sites, outdoor events, or areas without access to electricity. Gas air compressors can be easily moved and positioned where they are required.
2. Independence from Electricity:
One of the primary advantages of gas air compressors is their independence from electricity. They are powered by gas engines, which means they do not rely on a direct connection to the electrical grid. This makes them suitable for use in areas where electrical power is limited, unreliable, or unavailable. Gas air compressors offer a reliable source of compressed air even in remote locations or during power outages.
3. Versatility in Fuel Options:
Gas air compressors provide versatility in terms of fuel options. They can be powered by various types of combustible gases, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. This flexibility allows users to choose the most readily available or cost-effective fuel source based on their specific requirements. It also makes gas compressors adaptable to different environments and fuel availability in various regions.
4. Higher Power Output:
Gas air compressors typically offer higher power output compared to electric compressors. Gas engines can generate more horsepower, allowing gas compressors to deliver greater air pressure and volume. This higher power output is beneficial when operating pneumatic tools or equipment that require a significant amount of compressed air, such as jackhammers, sandblasters, or heavy-duty impact wrenches.
5. Continuous Operation:
Gas air compressors can provide continuous operation without the need for frequent breaks or cooldown periods. Electric compressors may overheat with prolonged use, requiring intermittent rest periods to cool down. Gas compressors, on the other hand, can operate continuously for longer durations without the risk of overheating. This continuous operation capability is particularly advantageous in demanding applications or situations that require extended periods of compressed air usage.
6. Quick Startup and Response:
Gas air compressors offer quick startup and response times. They can be started instantly by simply pulling a cord or pressing a button, whereas electric compressors may require time to power up and reach optimal operating conditions. Gas compressors provide immediate access to compressed air, allowing for efficient and prompt task completion.
7. Durability and Resistance to Voltage Fluctuations:
Gas air compressors are generally more durable and resistant to voltage fluctuations compared to electric compressors. Electric compressors can be affected by voltage drops or surges, which may impact their performance or cause damage. Gas compressors, however, are less susceptible to voltage-related issues, making them reliable in environments where voltage fluctuations are common.
8. Lower Energy Costs:
Gas air compressors can offer lower energy costs compared to electric compressors, depending on the price of the fuel being used. Gasoline or diesel fuel, for example, may be more cost-effective than electricity in certain regions or applications. This cost advantage can result in significant savings over time, especially for high-demand compressed air operations.
Overall, the advantages of using a gas air compressor over an electric one include portability, independence from electricity, fuel versatility, higher power output, continuous operation capability, quick startup and response times, durability, resistance to voltage fluctuations, and potentially lower energy costs. These advantages make gas air compressors a preferred choice in various industries, remote locations, and applications where mobility, power, and reliability are crucial.


editor by CX 2023-10-07
China wholesaler Best Air Compressor Machine Prices of Zp182kce-Tfd-425 15HP CHINAMFG Compresor Zp182 arb air compressor
Product Description
| R22 50HZ | SPEC. | |||||
| Model | Power(HP) | Displacement(m³/h) | ARI | Weight(KG) | Height(MM) (Including shock-absorbing strap) | |
| Capacity(W) | Input Power(W) | |||||
| One-Phase(220V-240V) | ||||||
| ZR28K3-PFJ | 2.33 | 6.83 | 6900 | 2520 | 26 | 383 |
| ZR34K3-PFJ | 2.83 | 8.02 | 8200 | 2540 | 29 | 406 |
| ZR34KH-PFJ | 2.83 | 8.02 | 8200 | 2540 | 29 | 406 |
| ZR36K3-PFJ | 3 | 8.61 | 8900 | 2730 | 29 | 406 |
| ZR36KH-PFJ | 3 | 8.61 | 8900 | 2730 | 29 | 406 |
| ZR42K3-PFJ | 3.5 | 9.94 | 15710 | 3140 | 30 | 419 |
| ZR47K3-PFJ | 3.92 | 11.02 | 11550 | 3460 | 32 | 436 |
| Three-Phase(380V-420V) | ||||||
| ZR28K3-TFD | 2.33 | 6.83 | 6900 | 2140 | 25 | 383 |
| ZR34K3-TFD | 2.83 | 8.02 | 8200 | 2500 | 28 | 406 |
| ZR34KH-TFD | 2.83 | 8.02 | 8200 | 2470 | 28 | 406 |
| ZR36K3-TFD | 3 | 8.61 | 8790 | 2680 | 29 | 406 |
| ZR36KH-TFD | 3 | 8.61 | 8300 | 2680 | 28 | 406 |
| ZR42K3-TFD | 3.5 | 9.94 | 15710 | 3100 | 28 | 419 |
| ZR47KC-TFD | 3.92 | 11.16 | 11550 | 2430 | 30 | 436 |
| VR61KF-TFP-542 | 5.08 | 14.37 | 14900 | 4636 | 28.5 | 436 |
| ZR61KC-TFD | 5.08 | 14.37 | 14600 | 4430 | 37 | 457 |
| ZR61KH-TFD | 5.08 | 14.37 | 14972 | 4440 | 35.9 | 457 |
| ZR68KC-TFD | 5.57 | 16.18 | 16900 | 4950 | 39 | 457 |
| ZR72KC-TFD | 6 | 17.06 | 17700 | 5200 | 39 | 457 |
| ZR81KC-TFD | 6.75 | 19.24 | 19900 | 5800 | 40 | 462 |
| VR94KS-TFP | 8 | 22.14 | 23300 | 6750 | 57 | 497 |
| VR108KS-TFP | 9 | 25.68 | 26400 | 7500 | 63 | 552 |
| VR125KS-TFP | 10 | 28.81 | 31000 | 9000 | 63 | 552 |
| VR144KS-TFP | 12 | 33.22 | 35000 | 15710 | 63 | 552 |
| VR160KS-TFP | 13 | 36.37 | 38400 | 11400 | 65 | 572 |
| VR190KS-TFP | 15 | 43.34 | 46300 | 13700 | 66 | 572 |
| ZR250KC-TWD | 20 | 56.57 | 60000 | 17700 | 142 | 736 |
| ZR310KC-TWD | 25 | 71.43 | 74000 | 22000 | 160 | 725 |
| ZR380KC-TWD | 30 | 57.5 | 92000 | 26900 | 176 | 725 |
| ZR81KC-TFD | 6.75 | 19.24 | 19900 | 5800 | 40 | 462 |
| VR94KS-TFP | 8 | 22.14 | 23300 | 6750 | 57 | 497 |
| VR108KS-TFP | 9 | 25.68 | 26400 | 7500 | 63 | 552 |
| VR125KS-TFP | 10 | 28.81 | 31000 | 9000 | 63 | 552 |
| VR144KS-TFP | 12 | 33.22 | 35000 | 15710 | 63 | 552 |
| VR160KS-TFP | 13 | 36.37 | 38400 | 11400 | 65 | 572 |
| VR190KS-TFP | 15 | 43.34 | 46300 | 13700 | 66 | 572 |
| ZR250KC-TWD | 20 | 56.57 | 60000 | 17700 | 142 | 736 |
| ZR310KC-TWD | 25 | 71.43 | 74000 | 22000 | 160 | 725 |
| ZR380KC-TWD | 30 | 57.5 | 92000 | 26900 | 176 | 725 |
| TECHNICAL DATA | |||||||
| Model | ZB15KQ | ZB19KQ | ZB21KQ | ZB26KQ | ZB29KQ | ZB38KQ | ZB45KQ |
| ZB15KQE | ZB19KQE | ZB21KQE | ZB26KQE | ZB29KQE | ZB38KQE | ZB45KQE | |
| Motor Type | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD |
| PFJ | PFJ | PFJ | PFJ | PFJ | |||
| Power(HP) | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Displacement(m³/h) | 5.92 | 6.8 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 11.4 | 14.5 | 17.2 |
| Starting Current(LRA) | |||||||
| TFD | 24.5-26 | 30-32 | 36-40 | 41-46 | 50 | 58.6-65.5 | 67-74 |
| PFJ | 53-58 | 56-61 | 75-82 | 89-97 | 113 | ||
| Rated Load Current(RLA) | |||||||
| TFD | 4.3 | 4.3 | 5.7 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 8.9 | 11.5 |
| PFJ | 11.4 | 12.9 | 16.4 | 18.9 | 19.3 | ||
| Max. Operating Current(MCC) | |||||||
| TFD | 6 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12.5 | 16.1 |
| PFJ | 16 | 18 | 23 | 24 | 27 | ||
| Motor Run | 40μF/370V | 40μF/370V | 55μF/370V | 60μF/370V | 60μF/370V | ||
| Crankcase Heater Power(W) | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Size of Connecting Pipe(INCH) | |||||||
| Outer Diameter of Wxhaust Pipe | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 |
| Outer Diameter of Suction Pipe | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 |
| Dimensions(MM) | |||||||
| Length | 242 | 242 | 243 | 243 | 242 | 242 | 242 |
| Width | 242 | 242 | 244 | 244 | 242 | 242 | 242 |
| Height | 383 | 383 | 412 | 425 | 430 | 457 | 457 |
| Foot Bottom Installation Dimensions(Aperture) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) |
| Fuel Injection(L) | 1.18 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.89 | 1.89 | 1.89 |
| Weight(KG) | |||||||
| Net.W | 23 | 25 | 27 | 28 | 37 | 38 | 40 |
| Gross.W | 26 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 40 | 41 | 44 |
| TECHNICAL DATA | |||||||
| Model | ZB48KQ | ZB58KQ | ZB66KQ | ZB76KQ | ZB88KQ | ZB95KQ | ZB114KQ |
| ZB48KQE | ZB58KQE | ZB66KQE | ZB76KQE | ||||
| Motor Type | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD | TFD |
| Power(HP) | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 15 |
| Displacement(m³/h) | 18.8 | 22.1 | 25.7 | 28.8 | 38.2 | 36.4 | 43.4 |
| Starting Current(LRA) | 101 | 86-95 | 100-111 | 110-118 | 110-118 | 140 | 174 |
| Rated Load Current(RLA) | 12.1 | 16.4 | 17.3 | 19.2 | 22.1 | 22.1 | 27.1 |
| Max. Operating Current(MCC) | 17 | 23 | 24.2 | 26.9 | 31 | 31 | 39 |
| Crankcase Heater Power(W) | 70 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | ||
| Size of Connecting Pipe(INCH) | |||||||
| Outer Diameter of Wxhaust Pipe | 3/4 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 | 7/8 |
| Outer Diameter of Suction Pipe | 7/8 | 11/8 | 13/8 | 13/8 | 13/8 | 13/8 | 13/8 |
| Dimensions(MM) | |||||||
| Length | 242 | 263.6 | 263.6 | 263.6 | 263.6 | 242 | 264 |
| Width | 242 | 284.2 | 284.2 | 284.2 | 284.2 | 285 | 285 |
| Height | 457 | 477 | 546.1 | 546.1 | 546.1 | 522 | 553 |
| Foot Bottom Installation Dimensions(Aperture) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) | 190X190(8.5) |
| Fuel Injection(L) | 1.8 | 2.51 | 2.25 | 3.25 | 3.25 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Weight(KG) | |||||||
| Net.W | 40 | 59.87 | 60.33 | 65.32 | 65.32 | 65 | 65 |
| Gross.W | 44 | ||||||
Archean refrigeration has been focusing on the refrigeration industry for more than 10 years. The compressors are sold all over the world and have been well received. The company has accumulated strong experience in the compressor market, rich technical support, and a satisfactory one-stop procurement solution. You can rest assured You don’t need to worry about this series, from placing an order to receiving the goods. We provide a complete solution to serve customers well, which is our purpose of hospitality.
| Installation Type: | Movable Type |
|---|---|
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Model: | Zp182kce-Tfd-425 |
| Transport Package: | Wooden/Cartoon Box |
| Specification: | 26*26*58CM |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for shipbuilding and maritime applications?
Air compressors are widely used in shipbuilding and maritime applications for a variety of tasks and operations. The maritime industry relies on compressed air for numerous essential functions. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are employed in shipbuilding and maritime applications:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Air compressors are extensively used to power pneumatic tools and equipment in shipbuilding and maritime operations. Pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches, drills, grinders, sanders, and chipping hammers require compressed air to function. The versatility and power provided by compressed air make it an ideal energy source for heavy-duty tasks, maintenance, and construction activities in shipyards and onboard vessels.
2. Painting and Surface Preparation:
Air compressors play a crucial role in painting and surface preparation during shipbuilding and maintenance. Compressed air is used to power air spray guns, sandblasting equipment, and other surface preparation tools. Compressed air provides the force necessary for efficient and uniform application of paints, coatings, and protective finishes, ensuring the durability and aesthetics of ship surfaces.
3. Pneumatic Actuation and Controls:
Air compressors are employed in pneumatic actuation and control systems onboard ships. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic valves, actuators, and control devices that regulate the flow of fluids, control propulsion systems, and manage various shipboard processes. Pneumatic control systems offer reliability and safety advantages in maritime applications.
4. Air Start Systems:
In large marine engines, air compressors are used in air start systems. Compressed air is utilized to initiate the combustion process in the engine cylinders. The compressed air is injected into the cylinders to turn the engine’s crankshaft, enabling the ignition of fuel and starting the engine. Air start systems are commonly found in ship propulsion systems and power generation plants onboard vessels.
5. Pneumatic Conveying and Material Handling:
In shipbuilding and maritime operations, compressed air is used for pneumatic conveying and material handling. Compressed air is utilized to transport bulk materials, such as cement, sand, and grain, through pipelines or hoses. Pneumatic conveying systems enable efficient and controlled transfer of materials, facilitating construction, cargo loading, and unloading processes.
6. Air Conditioning and Ventilation:
Air compressors are involved in air conditioning and ventilation systems onboard ships. Compressed air powers air conditioning units, ventilation fans, and blowers, ensuring proper air circulation, cooling, and temperature control in various ship compartments, cabins, and machinery spaces. Compressed air-driven systems contribute to the comfort, safety, and operational efficiency of maritime environments.
These are just a few examples of how air compressors are utilized in shipbuilding and maritime applications. Compressed air’s versatility, reliability, and convenience make it an indispensable energy source for various tasks and systems in the maritime industry.
.webp)
How does the horsepower of an air compressor affect its capabilities?
The horsepower of an air compressor is a crucial factor that directly impacts its capabilities and performance. Here’s a closer look at how the horsepower rating affects an air compressor:
Power Output:
The horsepower rating of an air compressor indicates its power output or the rate at which it can perform work. Generally, a higher horsepower rating translates to a greater power output, allowing the air compressor to deliver more compressed air per unit of time. This increased power output enables the compressor to operate pneumatic tools and equipment that require higher air pressure or greater airflow.
Air Pressure:
The horsepower of an air compressor is directly related to the air pressure it can generate. Air compressors with higher horsepower ratings have the capacity to produce higher air pressures. This is particularly important when operating tools or machinery that require specific air pressure levels to function optimally. For example, heavy-duty pneumatic tools like jackhammers or impact wrenches may require higher air pressure to deliver the necessary force.
Air Volume:
In addition to air pressure, the horsepower of an air compressor also affects the air volume or airflow it can provide. Higher horsepower compressors can deliver greater volumes of compressed air, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This increased airflow is beneficial when using pneumatic tools that require a continuous supply of compressed air, such as paint sprayers or sandblasters.
Duty Cycle:
The horsepower rating of an air compressor can also influence its duty cycle. The duty cycle refers to the amount of time an air compressor can operate continuously before it needs to rest and cool down. Higher horsepower compressors often have larger and more robust components, allowing them to handle heavier workloads and operate for longer periods without overheating. This is particularly important in demanding applications where continuous and uninterrupted operation is required.
Size and Portability:
It’s worth noting that the horsepower rating can also affect the physical size and portability of an air compressor. Higher horsepower compressors tend to be larger and heavier due to the need for more substantial motors and components to generate the increased power output. This can impact the ease of transportation and maneuverability, especially in portable or mobile applications.
When selecting an air compressor, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your intended applications. Factors such as desired air pressure, airflow, duty cycle, and portability should be taken into account. It’s important to choose an air compressor with a horsepower rating that aligns with the demands of the tools and equipment you plan to operate, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines can provide valuable information on how the horsepower rating of an air compressor corresponds to its capabilities and suitability for different tasks.
.webp)
What is the difference between a piston and rotary screw compressor?
Piston compressors and rotary screw compressors are two common types of air compressors with distinct differences in their design and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between these two compressor types:
1. Operating Principle:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors, also known as reciprocating compressors, use one or more pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress air. The piston moves up and down within a cylinder, creating a vacuum during the intake stroke and compressing the air during the compression stroke.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors utilize two intermeshing screws (rotors) to compress air. As the male and female screws rotate, the air is trapped between them and gradually compressed as it moves along the screw threads.
2. Compression Method:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors achieve compression through a positive displacement process. The air is drawn into the cylinder and compressed as the piston moves back and forth. The compression is intermittent, occurring in discrete cycles.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors also employ a positive displacement method. The compression is continuous as the rotating screws create a continuous flow of air and compress it gradually as it moves along the screw threads.
3. Efficiency:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors are known for their high efficiency at lower flow rates and higher pressures. They are well-suited for applications that require intermittent or variable air demand.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are highly efficient for continuous operation and are designed to handle higher flow rates. They are often used in applications with a constant or steady air demand.
4. Noise Level:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors tend to generate more noise during operation due to the reciprocating motion of the pistons and valves.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are generally quieter in operation compared to piston compressors. The smooth rotation of the screws contributes to reduced noise levels.
5. Maintenance:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors typically require more frequent maintenance due to the higher number of moving parts, such as pistons, valves, and rings.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance requirements. They often have longer service intervals and can operate continuously for extended periods without significant maintenance.
6. Size and Portability:
- Piston Compressors: Piston compressors are available in both smaller portable models and larger stationary units. Portable piston compressors are commonly used in construction, automotive, and DIY applications.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: Rotary screw compressors are typically larger and more suitable for stationary installations in industrial and commercial settings. They are less commonly used in portable applications.
These are some of the key differences between piston compressors and rotary screw compressors. The choice between the two depends on factors such as required flow rate, pressure, duty cycle, efficiency, noise level, maintenance needs, and specific application requirements.


editor by CX 2023-10-07
China 1.6-2.5M3Min 8 Bar 20HP Belt Compressor Combined 300L Air Tank 2.4M3Min Air Cooling Refrigerator Dryer arb air compressor
Relevant Industries: Constructing Material Outlets, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Restore Retailers, Meals & Beverage Factory, Farms, Restaurant, Brazil motorcycle chain sprocket kits kind YBR a hundred twenty five 03-09 Issue Home Use, Printing Stores, Construction works , Vitality & Mining, Food & Beverage Outlets, Promoting Company
Showroom Place: France
Situation: New
Kind: Screw
Configuration: Stationary
Electrical power Supply: AC Electricity
Lubrication Fashion: Lubricated
Mute: Of course
Design Quantity: OPA-20F/16
Voltage: 380V/220V/440V/415V
Dimension(L*W*H): eighteen Ec460 Ec240 1181-00681 Ec290 Ec210 Excavator Sprocket a lot more voltages)

A Buyer’s Guide to Air Compressor Types
There are many types of Air Compressors, and it’s important to understand what each type has to offer. In this article, we’ll discuss single stage air compressors, low-noise compressors, and models with two pistons. But, before you buy an Air Compressor, be sure to read our buyer’s guide to the various types. This way, you’ll have all of the information you need to make the right decision for your business.
Single-stage air compressors
A single-stage air compressor is an excellent choice for most general-purpose purposes. They provide enough power to operate pneumatic tools, and they produce less heat. Single-stage air compressors, however, are not suitable for heavy-duty industrial uses. However, they can be used in various applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing facilities. They are also suitable for borewells and other high-pressure places.
These air compressors are a great choice for home use and are suitable for small-scale businesses, contractors, and small shops. These compressors have continuous duty cycles, cast iron compressor pumps, and a minimum 5,000-hour pump life. They also feature advanced features, including ODP motors, Auto Start & Controls, Receiver tanks, and power cords. They have low maintenance and can save you a great deal of money.
Single-stage air compressors are generally less expensive and lighter than their two-stage counterparts. Single-stage air compressors are also more portable, which is a plus for small projects. While two-stage compressors offer higher CFM, they are more powerful and bulky, making them unsuitable for small or home use. So it is essential to determine what you will use the air compressor for and decide on a model based on your needs.
A single-stage air compressor is made of a piston and a tank. The piston moves rapidly inside the cylinder and exerts pressure on the cylinder. This means that the piston can’t move any faster than the air pressure outside the cylinder. The piston is designed to operate in the same way for each stage. This is a great choice for home shops and one-man automotive shops, as it allows you to control the pressure without sacrificing the pump’s life.
Single-stage air compressors are often cheaper than two-stage versions, but they are not the best choice for every application. If you are only using your air compressor occasionally, you’ll find a one-stage model to be much more reliable than a two-stage model. The main difference between the two types of compressors is in the amount of air that each stage compresses. A two-stage air compressor will have more air storage capacity, but it will still produce more pressure.
Rotary vane compressors
Rotary vane compressors use a centrifugal pump to compress air. The rotor is set eccentrically in the housing, which almost touches the vane. As the rotor turns, the air that enters the pump is trapped between the vanes. This compressed air undergoes compression as the rotor rotates. Vanes are small pieces of carbon fiber or graphite composite. Vanes may be made of different materials depending on the application.
While rotary vane pumps are not commonly used to produce compressed air, they are widely used in automotive and hydraulic applications. Chances are, you have used a rotary vane pump at some point in your life. These pumps are also common in the vacuum and compressed air industries. As a result, many people don’t realize that they’re still around. They feature slots that allow the vanes to slide in and out of the rotor.
A rotary vane compressor has a drum and rotor inside. The rotor is eccentrically positioned and has slots and grooves on its surface. Its inlet and outlet ports are situated off-center, allowing the vanes to be pushed out by centrifugal force. Because the rotor rotates so quickly, air is trapped between the vanes. This air then becomes pressurized by the rotating rotor.
Rotating vane compressors can be easily serviced and repaired. A simple replacement of carbon vanes requires just 15 minutes and common tools. The carbon vanes typically last nine to eighteen months, depending on system operating pressure. Before purchasing a rotary vane compressor, make sure to check whether it has been properly performance-tested and has a warranty. Generally, warranties cover the rotor/stator chambers but do not cover the vanes or air filters. You should also check if the unit is covered by a lightning or water damage warranty.
Rotary vane compressors are an integral part of manufacturing industries. Many pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities depend on rotary vane compressors to control their equipment. Other industries that use rotary vane compressors include the plastics, woodworking, natural gas, and medical & dental fields. Their benefits are numerous and far outweigh any disadvantages of rotary screw compressors. For example, a rotary vane compressor can double the life of a conventional compressor.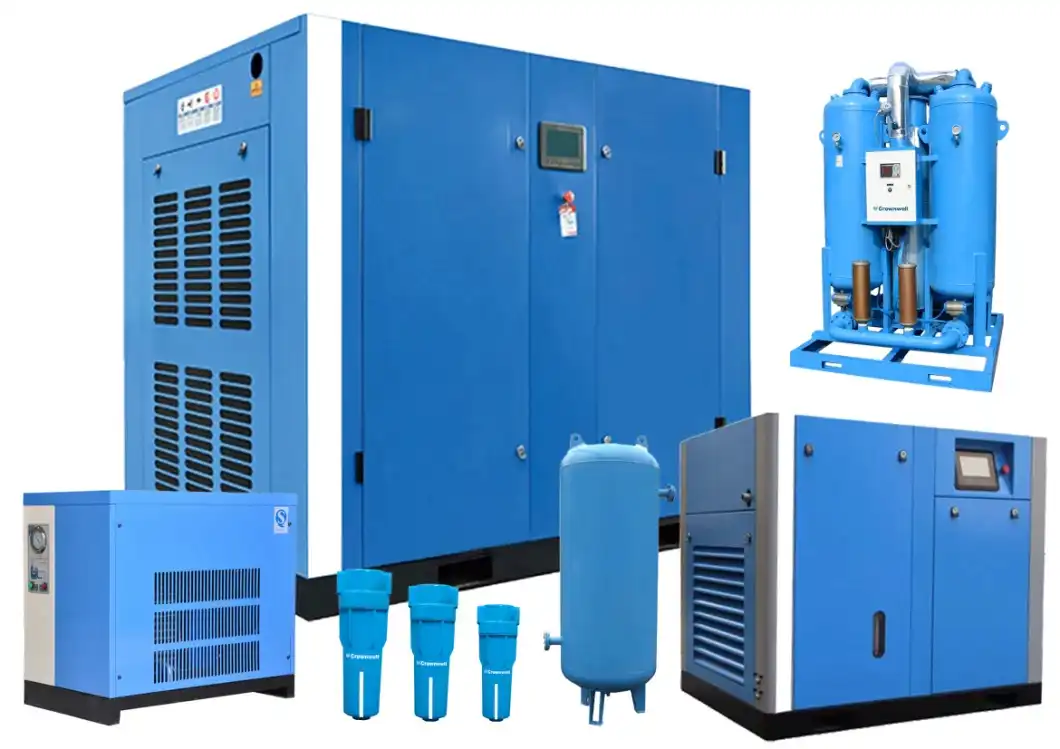
Rotary vane compressors with low-noise models
If you are looking for a rotary vane air compressor, you have come to the right place. CZPT’s LV Series rotary vane compressors offer low-noise models, compact size, and robust integration. In addition to their low-noise features, they feature large filter systems to deliver high-quality compressed air. The LV Series models also feature CZPT’s reputation for reliability and quality.
This type of compressor uses centrifugal force to operate and is limited in its top and minimum operating speeds. They are only a third as powerful as screw compressors, and their top speed limits are much lower. Furthermore, the vanes wear out easily at high speeds because there is not enough centrifugal force to seal them against the cylinder’s edges. Even at half their full capacity, they consume as much as 80% of their total energy rating.
Because piston compressors produce a lot of noise, factory owners and shop owners have begun to install noise-dampening cabinets and other solutions. But, rotary vane compressors produce far less noise than a traditional vacuum, and the maintenance costs are also low. Rotary vane compressors are also extremely helpful in several industries. They are used in the automotive and auto finishing industries, as well as in dairy industries and milking machines.
If you have a deep pond, a rotary vane air compressor kit can pump up to 20 feet of water. This is more than enough airflow for two to five diffusers. A 1/4 HP rotary vane kit pumps around 4.2 CFM. It also helps to increase circulation and oxygen levels in the pond. Finally, a 1/4 HP kit offers the necessary power to clean up the bottom of a pond.
The rotary vane and rotary screw are the most popular air compressors today. While they are similar in many ways, they are more versatile and durable than their counterparts. They use fewer angular contact ball bearings and require less frequent maintenance than piston air compressors. Compared to piston air compressors, rotary vane and rotary screw compressors are quieter and are less expensive.
Rotary vane compressors with two pistons
The rotary vane and rotary screw compressors are similar in application, but both have different advantages and disadvantages. This article will compare the benefits of each and highlight the differences between them. While both are commonly used in industrial applications, rotary vane compressors are preferred by many industries. These compressors also have a wide range of uses, ranging from automotive air tool operation to milking machines. These compressors also have the advantage of being quieter than piston-powered ones.
The current common rail position may not be suitable for pressure swirl injectors, but new positions have been tested and show improvements in specific energy values. Moreover, the current position is not required for external oil pumps. However, mass induction and expulsion have to be performed with utmost care. This article focuses on the design and efficiency of rotary vane compressors. You can find more information about this new design in the references mentioned below.
The advantages of this type of compressor are its low cost, compact size, and easy maintenance. Hence, they are preferred in low capacity applications. Moreover, they feature integrated vanes. The rotating vanes close the air gap and compress air towards the outlet. Compared to piston-powered compressors, these units are cheaper and more reliable. Therefore, you should choose one with the lowest price tag. You can also opt for rotary vane compressors that are oil-free.
Sliding vane compressors are another popular variant. They have a single cylinder connected to the compressor and are capable of operating at low speeds. This design also reduces the amount of friction and maintains volumetric efficiency. However, the sliding vane compressors suffer from high frictional losses. If you are looking for a more efficient rotary compressor, this is the best option. While sliding vane compressors have been in the spotlight for over a century, they are still quite young.
These compressors are easy to install and maintain. They are also quieter than piston compressors. They are also cheaper than piston-driven compressors. The energy efficiency and low price make them the perfect choice for any commercial or industrial application. If you’re looking for a small, compact compressor, the rotary vane has been proven to be the best choice for your needs. You should know that it has a long service life.


editor by Cx 2023-06-29
China Permanent Magnet Energy Saving 55kw Variable Speed Screw Air Compressor 75HP in Shanghai arb air compressor
Item Description
Long lasting Magnet energy preserving 55KW Variable speed screw air compressor 75HP In ZheJiang
Technological Knowledge:
|
Product |
WZS-75EVA |
|
Air Circulation/Functioning strain |
nine.7m3/min @ 8bar |
|
8.5m3/min @ 10bar |
|
|
Cooling type of COMPRESSOR |
Air cooling |
|
Cooling type of MOTOR |
Oil cooling |
|
Pushed strategy |
Integrated link |
|
Start off way |
Comfortable VSD Start |
|
VSD inverter |
INOVANCE / HOLIP / VEICHI |
|
Exhaust Temp. |
< ambient temp. +8 levels |
|
Oil articles |
<2ppm |
|
Sound |
69±2 dB(A) |
|
Power |
380VAC/3ph/~200Hz |
|
Motor power |
55kW/75hp |
|
Dimension |
1700*1270*1500mm |
|
Fat |
1350kg |
|
/ Peice | |
1 Peice (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Horizontal |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
|
Model |
WZS-75EVA |
|
Air Flow/Working pressure |
9.7m3/min @ 8bar |
|
8.5m3/min @ 10bar |
|
|
Cooling type of COMPRESSOR |
Air cooling |
|
Cooling type of MOTOR |
Oil cooling |
|
Driven method |
Integrated connection |
|
Start way |
Soft VSD Start |
|
VSD inverter |
INOVANCE / HOLIP / VEICHI |
|
Exhaust Temp. |
< ambient temp. +8 degrees |
|
Oil content |
<2ppm |
|
Noise |
69±2 dB(A) |
|
Power |
380VAC/3ph/0~200Hz |
|
Motor power |
55kW/75hp |
|
Dimension |
1700*1270*1500mm |
|
Weight |
1350kg |
|
/ Peice | |
1 Peice (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Cylinder Position: | Horizontal |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
|
Model |
WZS-75EVA |
|
Air Flow/Working pressure |
9.7m3/min @ 8bar |
|
8.5m3/min @ 10bar |
|
|
Cooling type of COMPRESSOR |
Air cooling |
|
Cooling type of MOTOR |
Oil cooling |
|
Driven method |
Integrated connection |
|
Start way |
Soft VSD Start |
|
VSD inverter |
INOVANCE / HOLIP / VEICHI |
|
Exhaust Temp. |
< ambient temp. +8 degrees |
|
Oil content |
<2ppm |
|
Noise |
69±2 dB(A) |
|
Power |
380VAC/3ph/0~200Hz |
|
Motor power |
55kW/75hp |
|
Dimension |
1700*1270*1500mm |
|
Weight |
1350kg |
Types of Air Compressors
There are many types of Air Compressors available on the market. Learn which one is right for your needs and what makes one better than another. Find out more about Single-stage models, Oil-free models, and Low-noise models. This article will explain these types and help you decide which one you need. You can also learn about Air Compressors that have single-stage compressors. If you are looking for a high-quality compressor, this article will help you choose a unit.
Air Compressors
Air compressors work by forcing atmospheric air through an inlet valve. As the piston moves down, it pulls atmospheric air into the chamber. As the piston rises, it forces the compressed air out of the cylinder through an exhaust valve. One of the most common types of air compressor is the reciprocating type. Another type of compressor is a single-stage piston. These types of compressors compress air in one stroke – equivalent to the complete rotation of the piston’s crankshaft.
These devices change electrical or mechanical energy into pressurized air. When air is compressed, its volume decreases, increasing its pressure. Air compressors typically have a minimum pressure of 30 bars. The lower pressure band is the range of air pressure. Most compressors are controlled separately, but network controls can be used to interconnect multiple compressors. This type of controller will not work for all types of compressors. There are other types of air compressors that can communicate with each other.
Compressed air has multiple applications in all kinds of industries. In agriculture, it can power pneumatically powered material handling machines for irrigation and crop spraying. Dairy equipments also use compressed air. Compressors are also used in the pharmaceutical industry for mixing tanks, packaging, and conveyor systems. Portable air compressors, which can be powered by diesel fuel, are frequently used at remote drilling sites. Portable air compressors are also commonly used in oil and gas. They can be used to remotely control valves and install reactor rods.
Whether you use an air compressor for agricultural purposes or in a manufacturing setting, there are some features to consider when choosing an air compressor for your needs. A good compressor will have a safety device. It will automatically shut off the input air and output air once sufficient compressing has been achieved. These features will help your air compressor remain efficient and protect your equipment. The safety device is an important feature of any air compressor to increase its overall efficiency.
Vane air compressors are the most common type. They are generally smaller and less powerful than reciprocating piston compressors, so you can use one of these for applications that are under 100 horsepower. The vane air compressors have low compression ratios and high capacities, but they are generally limited to low-power applications. Vane compressors tend to run hot, and they typically have a low compression ratio. It is important to choose the correct oil viscosity for your compressor.
Single-stage models
When comparing single-stage air compressors, look for the term “stages.” Multi-stage compressors use two stages and can handle more capacity and pressure. One stage involves pressurizing air using a piston and a lower-pressure cylinder. This compressed air is then moved to a storage tank. Single-stage models tend to be more energy-efficient than their two-stage counterparts. But if you don’t need a high-pressure cylinder, a single-stage air compressor can be the best choice.
Although single-stage air compressors produce less power, they can produce enough air to power pneumatic tools and other pneumatic equipment. These single-stage units are most useful for smaller-scale home projects and DIY projects. For more industrial purposes, a dual-stage model is the best choice. But if you’re in a hurry, a single-stage unit may be sufficient. Ultimately, it depends on what you plan to do with the air compressor.
Single-stage air compressors feature a single cylinder, one piston stroke for each revolution of pressurized air. Single-stage compressors are typically smaller and more compact, making them a good choice for smaller work environments. Their cfm capacity (cubic feet per minute) is an important indicator of operating capacity. If you plan to use multiple pneumatic tools, you will probably need a higher cfm model. Similarly, the horsepower of single-stage compressors indicates its working capacity. One horsepower moves 550 pounds per foot per minute.
Multi-stage air compressors are generally more expensive and more energy-efficient than single-stage units, but they can offer higher air flow rates. While they may be more complex, they can lower general operating expenses. If you plan on using your air compressor for industrial or commercial use, a dual-stage model might be the best choice. However, if you’re planning to use the air compressor for mass production, a single-stage model may be the best choice.
Single-stage air compressors have the same piston size and number of inlets, while dual-stage models have a smaller first piston and a much longer second piston. Both have a cooling tube in between the two pistons to reduce the air temperature before the second round of compression. The single-stage model is typically small and portable, while the double-stage air compressor is stationary. These compressors can both be stationary and large.
Low-noise models
Despite its name, low-noise models of air compressors are not all the same. The noise level of a compressor can be affected by several factors, including the power source and proximity to the machine. Reciprocal compressors are generally louder than electric ones because of their many moving parts. By contrast, rotary-screw and scroll compressors have fewer moving parts and are quieter.
The noise level of a gas-powered air compressor can be extremely high, making it unsuitable for use indoors. To combat this problem, you can choose an electric model. The noise level of a compressor is primarily caused by motor friction. The cover of a piston is also a major factor in noise, as pistons with minimal covers will produce a lot of noise. Previously, oil was required for a quiet compressor. However, this has changed thanks to the medical industry’s demand for oil-free models.
The CZPT EC28M Quiet Air Compressor is another model that features quiet operation. This air compressor makes 59dB of noise. This level is low enough to allow you to carry on normal conversations while it cycles. In addition, this compressor has an industrial oil-free pump and a 2.8 Amp direct-drive induction motor. These two features make it a great choice for businesses.
Low-noise models of air compressors are available for the construction industry. However, these compressors are not necessarily low-quality, which is why you should consider the noise level of your air tool before purchasing one. The specialists at CZPT can recommend the low-noise models for your particular application and space. Noise can distract people who work near the air compressor. That is why many businesses now opt for these models.
Oil-free models
A number of oil-free models of air compressors are available, but what makes them special? Oil-free compressors don’t contain oil, so they’re lubricated by grease instead. They’re a good choice if you’re working with a small compressor and don’t want to risk damaging it. On the other hand, oil-free models do generate significant amounts of heat, which can damage the compressor. Higher pressure can grind the compressor against itself, or even warp it.
A few words of knowledge can help you choose the best oil-free air compressor for your needs. For example, a compressor’s horsepower is a measurement of how powerful the motor is. Higher horsepower means a higher PSI or ACFM. You can also use the ACFM to compare the two. Scroll technology is a modern air compression system that uses a stationary and mobile spiral. This reduces the volume of air in the compressor by directing it to the center.
Purchasing an oil-free air compressor doesn’t have to be a daunting task, though. A good distributor can advise you on what type of oil-free air compressor is right for you. This way, you can save money and enjoy peace of mind while using your air compressor. And, of course, the best way to get a great deal on an air compressor is to speak to a distributor who is knowledgeable about the products available.
An oil-free air compressor is a great option for businesses that are sensitive to the contamination of air. For example, in the pharmaceutical and food industry, a minuscule oil could spoil a product or even damage production equipment. Oil-free air compressors generally have lower maintenance costs than oil-flooded models because there are fewer moving parts. Because of this, oilless air compressors require fewer maintenance and may still need to be replaced occasionally.
A few advantages of an oil-free air compressor over an oil-lubricated one include lower noise levels. Oil-free air compressors tend to be less noisy and run more quietly than oil-injected ones, but you should still carefully weigh the pros and cons before making a decision. Also, consider how much you use your air compressor before choosing a model. The pros outweigh the cons. In the end, you’ll be glad you chose an oil-free air compressor.


editor by CX 2023-03-31
China Kaishan Bk-11/55 Diesel Air Compressor arb air compressor
Solution Description
Merchandise Description
KaiShan LGZJ-35/twenty five Diesel Screw Air Compressor
CZPT screw air compressors, supplying the industry’s high regular of operating performance and assembly a extensive variety of building needs in the market. It adopts substantial compression performance screw primary motor, powerful brand motor, air volume handle system to meet a wide selection of requirements and effective cooling system for superb functionality and trustworthiness.
FAQ:
Q1: Are you a factory or trade organization?
A1: We are a manufacturing unit. And we have ourselves investing business.
Q2: What is the exact deal with of your manufacturing facility?
A2: Our firm is situated in No.625, Century Avenue, HangZhou, ZHangZhoug, China
Q3: Guarantee terms of your device?
A3: One-12 months warranty for the machine and complex assistance in accordance to your wants.
This autumn: Will you supply some spare areas for the machines?
A4: Of course, of program.
Q5: What about the voltage of merchandise? Can they be customized?
A5: Sure, of program. The voltage can be personalized according to your specifications.
Q6: Which payment phrase can you accept?
A6: 30% T/T in innovative, 70% T/T in opposition to the B/L copy.
Q7: How prolonged will you get to organize production?
A7: 380V 50HZ we can supply the goods within 7-fifteen days. Other electricity or yet another shade we will supply within 25-30 times.
Q8: Which trade term can you take?
A9: Offered trade conditions: FOB, CIF, CFR, EXW, CPT, and many others.
|
/ Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Power Source: | Diesel Engine |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
|
/ Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Power Source: | Diesel Engine |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
The Air Compressor Is a Versatile Tool
The Air Compressor is one of the most versatile tools in any garage or workshop. It is easy to use and can perform a variety of tasks, from jackhammering to drilling. These machines are available in a wide variety of sizes and types, making it an excellent choice for a variety of situations. With a single motor, you no longer need separate motors for each tool. Its lightweight, compact design makes it easy to handle, and the single motor also reduces wear on parts.
Oil-injected
Oil-injected air compressors require a large amount of lubricant, which needs to be added to the sump regularly to maintain optimum performance. As there are many types of industrial fluids, a well-intentioned maintenance technician may add the wrong lubricant to the compressor. If this happens, the compressor will become incompatible with the lubricant, resulting in excessive carryover and the need to flush and replace downstream air treatment components.
Typically, the G 110-250 oil-injected rotary screw compressor from Atlas Copco provides reliable compressed air, preventing costly downtime. The G110-250 oil-injected rotary screw compressor is highly reliable and durable, enabling it to function in temperatures up to 46degC/115degF. Despite the oil-injected air compressor’s robust design, this unit requires very little on-site installation, and it features simple operation.
The primary advantage of oil-injected air compressors is the reduced cost of running. The cost of oil-free compressors is less than half of that of oil-injected ones, and it will require fewer maintenance costs in the long run. Moreover, the oil-free system is more environmentally friendly than oil-injected air compressors. But the drawbacks of oil-injected air compressors are substantial, too. It can contaminate finished goods and cause a significant financial risk for the manufacturer.
An oil-injected rotary screw air compressor offers several advantages over its counterpart. First, it features an innovative vertical design with variable-speed drive, allowing it to run more efficiently. Second, oil-injected air compressors reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to non-oil-injected air compressors. They also have a thermostatic valve, allowing them to maintain an optimum temperature. Thermostatically-regulated oil coolers allow the compressor to run more quietly.
Oil-free
What is an oil-free air compressor? The name refers to a type of air compressor that does not contain oil in the compressor chamber. Oil-free air compressors still use oil for various purposes, including lubricating the moving parts and managing waste heat. However, many people do not realize that their air compressor still requires oil for proper functioning. This article will explore why this type of air compressor is preferable for many users.
First of all, oil-free air technology has many benefits. For one, it reduces the energy cost involved in filtering air, and it minimizes leaks. Moreover, it also reduces the oil costs associated with compressor refills. And finally, it reduces the risks of contamination. Oil-free air technology is the future of compressed air. If you’re looking for an oil-free air compressor, here’s what to look for in your search.
Depending on the purpose of your air compressor, it may be beneficial to invest in an oil-free air compressor. Oil-lubricated air compressors are generally more durable than their oil-free counterparts, but they may cost twice as much. You should still consider the cost of ownership before purchasing an oil-free compressor. The oil-free models can be easier to transport, and they are more powerful. Moreover, they’re quieter than oil-lubed models.
An oil-free air compressor also means less maintenance, as it doesn’t need oil to work. This type of air compressors also features fewer moving parts, which means fewer places for problems to develop. All oil-free air compressors are manufactured to meet ISO Class 0 and 1 air purity standards. They also have less noise and vibration compared to their oil-based counterparts. So, why not choose an oil-free air compressor for your business?
Gasoline
When choosing a gas-powered air compressor, it’s important to consider the advantages of gasoline. This energy source can power a large air compressor without electricity. However, this type of air compressor lacks electrical hookup, so you’ll need to run an extension cord if you need to use it at a distance. However, gas compressors are able to function with just a gas tank. This makes them ideal for medium to heavy-duty industrial applications.
Another important consideration when choosing a gas air compressor is its size. Larger compressors are typically larger than portable ones and require more space. This makes them easier to transport and operate on the go. However, if you’re not sure which type of air compressor is best for you, consider the gas-powered versions. While they may be lighter, they don’t run as smoothly as their electric counterparts. Gasoline-powered compressors are not as portable as their electric counterparts and require proper maintenance.
Electricity
Electricity in an air compressor is not cheap. A 25 HP air compressor runs for ten hours each day, five days a week. The motor in these machines consumes 746 watts per hour. To find out how much electricity the equipment uses, multiply the wattage by the running time. For example, if the compressor runs for three hours, then it will use 1.9 kilowatt hours of electricity. To determine how much electricity an air compressor uses per day, you can calculate the kilowatt hours and multiply the number by the utility rate. Considering this, you can determine the cost of running your air compressor once per month.
The cost of operating an air compressor depends on the type of compressor. Electric air compressors are often silent and can run without any maintenance. These tools can be left unattended for up to four thousand hours before requiring repair. Electric air compressors require higher power for higher pressure, so you should plan accordingly. Whether or not you need a maintenance visit is up to you, but the benefit of not having to spend a fortune on repairs is priceless.
Although compressed air is not an energy-efficient source, its use in a variety of applications may save you money and kilowatts. Since an air compressor uses power when it is running, the cost is lower than the cost of operating a power tool. If you plan to use your air compressor for a long time, make sure that it is maintained properly. Proper care will save you money and power, and you may even be able to get an extended warranty if the compressor breaks down.
Variable frequency drive
The main purpose of a variable frequency drive (VFD) in an air compressor is to reduce energy consumption in the process of compression. A single motor drag system cannot adjust its speed continuously according to the weight of the load. By applying frequency control to the compressor, the power consumption can be reduced while maintaining the same pressure level. Therefore, a VFD is an excellent choice for compressors. Its benefits are numerous.
A VFD can also monitor the temperature of the motor and send error signals if the motor is running too hot or too cold. This eliminates the need for a separate sensor to monitor the oil pressure. These functions are useful not only in lowering energy consumption, but also in improving the performance of an application. Moreover, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as temperature and motor speed. Hence, it is a useful investment.
When using a VFD, it is crucial to choose the right motor. The speed of the compressor should be within the maximum starting limit of the motor. The air tank may be of any size, but a constant pressure limit is required to keep the VFD running within the service factor of the motor. In addition to a VFD, a master controller should also include a remote pressure set point and a PID card for a master controller. The transmitter should incorporate all useful data from the VFD, including the speed and the oil temperature. The VFD must be tested before it is integrated with the master control. It should be tested for min and max speed, temperature, and current within the expected range.
The use of a VFD in an air compressor has many benefits. One of the most notable is the reduction in power consumption. Fixed-speed compressors run on set points of six to seven bar. An extra bar of compression uses 7 percent of energy. This energy is wasted. A VFD-powered air compressor can also increase the life span of compressor parts. It is one of the best investments in your compressor. So, why wait any longer?


editor by CX 2023-03-27
China 14.5 Bar 600 Cfm 90kw Electric Air Compressor Used for Mine arb air compressor
Merchandise Description
1. Our solitary-stage rotary screw airend and rotor is huge which permits for larger bearings, 30%~fifty% slower rotor speeds results in considerably less electrical power intake or sounds or maintenance expense.
two. 1 piece bearing housing makes certain each rotors are held by the bearings in proper alignment during transient durations such as device startups/shutdowns or load adjustments.
three. All of our air compressors have the latest inlet valve, airend air discharge port and oil inlet port design.
four. Decrease seem emission amount than most of our competition results in considerably less seem pollution.
5. The axial and rotational loading are supported by various bearings for much better stiffness and considerably less transition noise.
six. Basic package deal layout requires only bare minimum servicing for optimum functionality. Ongoing cooling and circulation of lubrication oil, assures lengthy airend operation existence.
Item Functions
1> Far more stunning apprance, excellent anti-corrosion efficiency
2> Exhaust pipe is set in the path situation, more environmental-helpful
3> Part position and road technique framework is a lot more affordable
4> Import solenoid valve (progress configuration)
5> Imported oil filter and tailored oil and gasoline separator filter (Germany Mann)
6> Higher Configuration of pipeline connection details components
Specifications
| Product | Exhaust pressure (Mpa) |
Exhaust volume (m³/min) |
Motor power (KW) |
Exhaust link |
Weight (kg) |
Dimension (mm) |
| KSDY-thirteen.6/eight | .8 | 13.six | seventy five | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-twelve.5/10 | 1. | twelve.five | seventy five | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-10/fourteen.five (Two rounds) |
one.forty five | 10 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1600 | 2500×1530×1700 |
| KSDY-16.5/8 | .eight | 16.5 | ninety | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1940 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-13/14.5 (Two rounds) |
one.45 | thirteen | ninety | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1760 | 2700×1670×1800 |
| KSDY-13/fourteen.five (Four rounds) |
one.forty five | 13 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1910 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-twenty/8 | .eight | 20 | a hundred and ten | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3115 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-16.5/twelve | one.2 | sixteen.5 | a hundred and ten | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3000 | 3065×1835×20000 |
| KSDY-24/eight | .8 | 24 | 132 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3150 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-18/thirteen | one.3 | eighteen | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3070 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY15/17 | one.seven | fifteen | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 2975 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-20/18-II | 1.eight | 20 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3700 | 3400×1620×2200 |
| KSDY-22/18-II | one.eight | 22 | 132-4 level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3100 | 3400×1620×2200 |
Specifics Photo
Air volume computerized management program
In accordance to the functioning strain, the air volume adjustment device instantly and steplessly adjusts the air compressor suction quantity and the diesel engine velocity. Entirely match the air supply and intake, so as to accomplish the greatest final results with the lowest gas usage.
Lower noise procedure
Silent protect style, reduced functioning noise, and the device style are more environmentally friendly.
SKY patented line, high power preserving
The special rotor tooth profile supplies excellent overall performance for every single sort of handpiece modern layout, optimized construction, and high-dependability performance.
Open design and style, simple maintenanca
The roomy opening doorways and windows make it very handy to keep the air filter, oil filter, and oil separator core. The components to be fixed are all inside reach, reducing downtime and maintenance time.
Why Pick Us
In 2009, CZPT proven Jersey North American Research Heart in Seattle in the United States, attracting many top-notch compressor professionals from all around the entire world and producing a new product that is aptly described as “created in The united states, Made in China”
Kaishan is headquartered in HangZhou in ZHangZhoug, China. It has subsidiaries in ZheJiang , Chgonqing, ZheJiang , ZheJiang , Hong Kong, Seattle, San Diego, Orlando, Melbourne, Singapore, Jakarta, Leobersdorf, Budapest and Belgrade, as well as places of work in Russia, Colombia, Brazil, Korea, Malaysia and Thailand.
Solution high quality is strictly controlled
Packaging and Delivery
The air compressor is guaranteed for 1 yr. In addition to sporting elements and consumables, if the spare parts inside the warranty period of time are broken, the firm offers totally free spare components replacement, but the purchaser needs to shell out the freight. You should request client provider for specific guarantee rules.
FAQ
Q1: Are you a manufacturing unit or trade organization?
A1: We are a factory. And we have ourselves trading organization.
Q2: What is the actual deal with of your manufacturing facility?
A2: Our company is located in JNo.9 Kaixuan Ave West, Financial Zone HangZhou, ZHangZhoug, China
Q3: Guarantee phrases of your machine?
A3: 1-yr guarantee for the device and technical help according to your needs.
This autumn: Will you supply some spare elements for the equipment?
A4: Sure, of course.
Q5: What about the voltage of merchandise? Can they be personalized?
A5: Of course, of course. The voltage can be tailored according to your needs.
Q6: Which payment expression can you settle for?
A6: 30% T/T in sophisticated, 70% T/T from the B/L copy.
Q7: How long will you take to organize production?
A7: 380V 50HZ we can supply the goods within 7-fifteen days. Other electricity or yet another color we will delivery inside of 25-thirty days.
Q8: Can you settle for OEM orders?
A8: Yes, with a skilled design crew, OEM orders are hugely welcome.
Q9: Which trade expression can you acknowledge?
A9: Accessible trade conditions: FOB, CIF, CFR, EXW, CPT, and so on.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| After-sales Service: | One Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
###
| Model | Exhaust pressure (Mpa) |
Exhaust volume (m³/min) |
Motor power (KW) |
Exhaust connection |
Weight (kg) |
Dimension (mm) |
| KSDY-13.6/8 | 0.8 | 13.6 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-12.5/10 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-10/14.5 (Two rounds) |
1.45 | 10 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1600 | 2500×1530×1700 |
| KSDY-16.5/8 | 0.8 | 16.5 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1940 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-13/14.5 (Two rounds) |
1.45 | 13 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1760 | 2700×1670×1800 |
| KSDY-13/14.5 (Four rounds) |
1.45 | 13 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1910 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-20/8 | 0.8 | 20 | 110 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3115 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-16.5/12 | 1.2 | 16.5 | 110 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3000 | 3065×1835×20000 |
| KSDY-24/8 | 0.8 | 24 | 132 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3150 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-18/13 | 1.3 | 18 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3070 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY15/17 | 1.7 | 15 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 2975 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-20/18-II | 1.8 | 20 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3700 | 3400×1620×2200 |
| KSDY-22/18-II | 1.8 | 22 | 132-4 level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3100 | 3400×1620×2200 |
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| After-sales Service: | One Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
###
| Model | Exhaust pressure (Mpa) |
Exhaust volume (m³/min) |
Motor power (KW) |
Exhaust connection |
Weight (kg) |
Dimension (mm) |
| KSDY-13.6/8 | 0.8 | 13.6 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-12.5/10 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1750 | 2700×1700×1700 |
| KSDY-10/14.5 (Two rounds) |
1.45 | 10 | 75 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1600 | 2500×1530×1700 |
| KSDY-16.5/8 | 0.8 | 16.5 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1940 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-13/14.5 (Two rounds) |
1.45 | 13 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1760 | 2700×1670×1800 |
| KSDY-13/14.5 (Four rounds) |
1.45 | 13 | 90 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 1910 | 2730×1680×1800 |
| KSDY-20/8 | 0.8 | 20 | 110 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3115 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-16.5/12 | 1.2 | 16.5 | 110 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3000 | 3065×1835×20000 |
| KSDY-24/8 | 0.8 | 24 | 132 | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3150 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-18/13 | 1.3 | 18 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3070 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY15/17 | 1.7 | 15 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 2975 | 3065×1835×2000 |
| KSDY-20/18-II | 1.8 | 20 | 132-2level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3700 | 3400×1620×2200 |
| KSDY-22/18-II | 1.8 | 22 | 132-4 level | G2×1,G¾×1 | 3100 | 3400×1620×2200 |
Choose an Air Compressor for Your Business
There are several factors to consider when choosing an air compressor for your business. One factor to consider is the type of compressor you are looking for, which may include single-stage, low noise, and positive displacement. Hope this article helps you make the right decision. After all, your business success will depend on this device! Let’s take a closer look at these factors. Also, consider what compressor manufacturers say about their products.
Positive displacement
Positive displacement air compressors compress air by drawing in a volume from an inlet and extruding it out of a chamber. This increases the pressure at which the gas can be pumped at rates that cannot be pumped through the outlet at lower pressures at higher mass flow rates. These types of compressors are available in single-acting and double-acting configurations. They are classified by the number of cylinders.
There are two different types of air compressors: reciprocating air compressors and screw compressors. Both are roll machines. Positive displacement air compressors use pistons and cylinders to compress air. The resulting air pressure builds up within the compressor housing, increasing the potential energy of the compressed air. Screw air compressors are the most popular positive displacement air compressors, which can be either single-stage screw-blade air compressors or multi-stage screw-blade oil-immersed screw air compressors.
Positive displacement flowmeters use a rotating measuring chamber to divide the fluid into discrete quantities. The number of times the chamber was refilled and emptied was used to estimate the total flow. However, positive displacement flow meters are prone to leaks, reducing the accuracy of the estimates. If a leak occurs, it can cause false readings and damage the compressor. However, leaks in positive displacement air compressors can reduce pressure.
The most common types of positive displacement air compressors are screw, reciprocating, and vane. Rotary positive displacement air compressors are also available as well as many other air compressors. Positive displacement air compressors are most commonly used in large manufacturing facilities. If you are considering an air compressor for commercial or industrial applications, it is imperative to understand how the components of the unit work. Please read the information below to learn more before deciding which application is best for you.
Positive displacement air compressors use a piston to force air into a chamber, compressing the air in the process. The piston moves in the opposite direction, thereby reducing the volume of the chamber. When the amount of air in the chamber reaches its maximum value, the valve opens, allowing it to escape at higher pressure. Positive displacement air compressors are generally less efficient than centrifugal compressors. However, they are still an excellent choice for a variety of applications.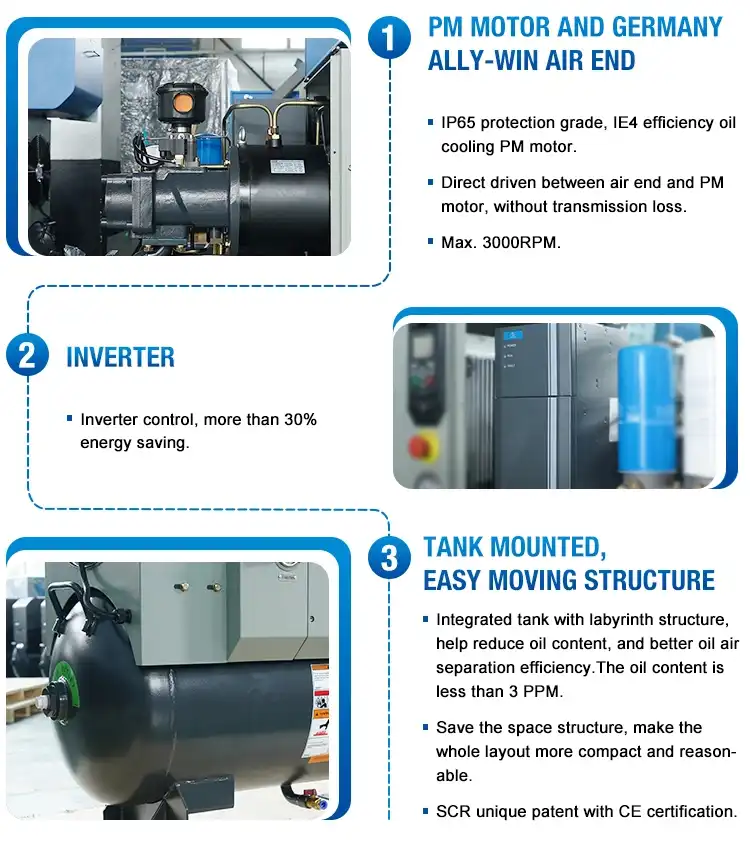
Single-stage
The discharge pressure of the single-stage air compressor is used to control the operation of the compressor. Properly designed load/unload controls allow the air compressor to operate at its most efficient point while minimizing stress on the main engine bearings. Single-stage air compressors can approach variable speed efficiency with appropriate storage capacity. However, improper storage can cause premature bearing wear on the main unit. If this is the case, a single-stage air compressor may not be ideal.
A single-stage air compressor has only one cylinder, which means one stroke is required to move air from one cylinder to another. Pressure is measured in cubic feet per minute or CFM. Tank size is also important as a large single-stage air compressor may be required to operate multiple air tools. Single-stage air compressors can be used in a variety of applications and can last for years.
For the most common uses, single-stage air compressors are the most practical option. These devices work with most hand tools, from hammers to grinders. Single-stage air compressors are lightweight and easy to move. However, two-stage air compressors provide more CFM, making them a better choice for industrial or commercial use. However, two-stage compressors are not suitable for private use. Therefore, if your main purpose is DIY and craft projects, it is better to choose a single-stage air compressor.
Compared with two-stage air compressors, single-stage screw air compressors are cheaper. They come from a variety of manufacturers and range in power from 3 to 600 horsepower. Single-stage air compressors are a cost-effective solution for a variety of air compressor needs. They offer flexibility and multiple control methods, making them an excellent choice for many different applications. Therefore, when choosing an air compressor for your business, choose the one with the most suitable functions.
Single-stage air compressors are the most affordable and easy-to-use air compressors for small to medium jobs. They also have higher compression ratios. The compression ratio is the ratio of absolute discharge pressure to absolute inlet pressure. When calculating the ratio, it takes into account atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure. The compression ratio pushes the surface area of the rotor, which increases the thrust load.
Single-stage air compressors are smaller and easier to transport than two-stage units. Single-stage air compressors have one air intake, and two-stage air compressors have two air intakes. The difference between single-stage and two-stage air compressors largely depends on the number of times the air is compressed. A single-stage air compressor compresses the air once, while a dual-stage air compressor compresses the same amount of air twice.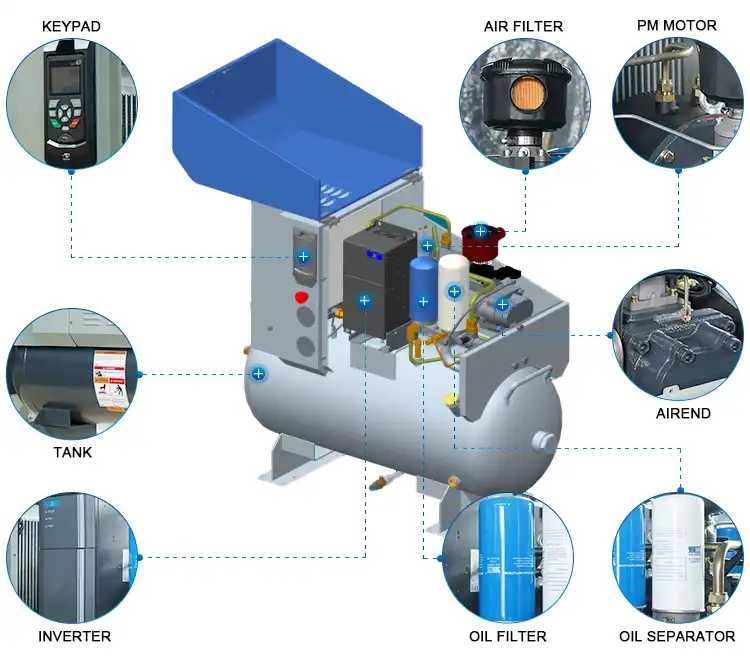
low noise
Low noise air compressors are ideal for a variety of applications. While no air compressor is completely silent, some models are much quieter than others. For the Hitachi EC28M portable compressor, the noise level is 59 decibels. The compressor features steel rollers that protect the internal components and give it a sleek, modern look. It also has a one-gallon fuel tank and a half-horsepower drive.
Noise from air compressors can be distracting and reduce productivity. It is important to choose low-noise air compressors to keep employees healthy and happy at work. While noise is an unfortunate aspect of working on the shop floor, reducing it can improve productivity. By reducing distracting noise, employees can focus on their work and communicate more effectively. That means higher quality work and happier clients. If you’re looking for a low-noise air compressor, be sure to read the tips below.
Low noise air compressors are an excellent choice for businesses of all sizes. These powerful tools can run multiple tools simultaneously. The two water tanks are made of rust-resistant aluminum and are stackable. This air compressor is heavier and can handle large jobs with ease. It costs more than other air compressors, but it can handle a lot of work efficiently. CZPT Air Tools air compressors come with a one-year warranty and are highly recommended by contractors.
Noiseless air compressors are generally more expensive than comparable products, but they are worth the extra cost. Noiseless compressors are a good option for businesses that need to avoid disturbing nearby people. For example, you might want to consider a low-noise air compressor for a dental office, which cannot tolerate noise. Fortunately, this problem can be solved by relocating the compressor to a location that is more isolated from your workspace.
One brand of low-noise air compressors offers two models. The CZPT Air Tools 2010A features a large cast aluminum can, regulating pressure gauge, and two universal quick-connects. It produces 68 decibels of noise when it works. It has a large 8-gallon fuel tank capacity and has wheels and handles for easy transport. Its powerful engine produces a low noise level of 68 decibels.
Another popular low noise air compressor is the Makita MAC210Q Quiet Series. This model is capable of producing up to 71.5 decibels of sound, which is the amount of air it produces at 90PSI. The MAC210Q features a durable oil-free pump and weighs just 36 pounds with a handle and wheels. These compressors are easy to move and ideal for indoor work.

editor by CX 2023-03-27